Determine the reactions hinges A and D exert on the frame and the force in each two force member. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right and the +y-axis is up along the page. Enter forces in pounds 320 Ib/ft AAA B D 4 ft magnitude Ib direction The magnitude is zero. V magnitude X Ib direction Enter a number. magnitude Ib direction The magnitude is zero. magnitude X Ib direction Far magnitude X Ib sense compression magnitude x Ib sense tension
![**Problem Statement:**
Determine the reactions hinges A and D exert on the frame and the force in each two-force member. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right and the +y-axis is up along the page. Enter forces in pounds.)
**Diagram:**
The diagram presents a horizontal frame with a uniformly distributed load of 320 lb/ft acting across a 4-foot length from point B to point C. The frame is supported by hinges at points A and D. Distances are marked as follows:
- From A to B: 2 ft
- From B to C: 4 ft
- From C to D: 2 ft
Vertical members E and F connect the horizontal beam to hinges A and D, respectively.
**Force Calculations:**
1. \( \vec{A}_x \)
- Magnitude: 0 lb
- Direction: The magnitude is zero.
2. \( \vec{A}_y \)
- Magnitude: [Enter a number]
- Direction: [Selection required]
3. \( \vec{D}_x \)
- Magnitude: 0 lb
- Direction: The magnitude is zero.
4. \( \vec{D}_y \)
- Magnitude: [Enter a number]
- Direction: [Selection required]
5. \( F_{BE} \)
- Magnitude: [Enter a number]
- Sense: Compression
6. \( F_{CF} \)
- Magnitude: [Enter a number]
- Sense: Tension
**Instructions:**
- Input values for \( \vec{A}_y \), \( \vec{D}_y \), \( F_{BE} \), and \( F_{CF} \) using the appropriate sense (tension or compression) and consider the indicated direction for forces.
- Calculate reactions considering equilibrium conditions for the system.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbf4a0e0b-2125-467b-b1bc-8bc81e995df8%2F67a6a807-6f6a-4fba-8a36-761c731942c3%2Fyc7elyg_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Member BCD.
The following figure shows the Free Body Diagram of Member BCD.
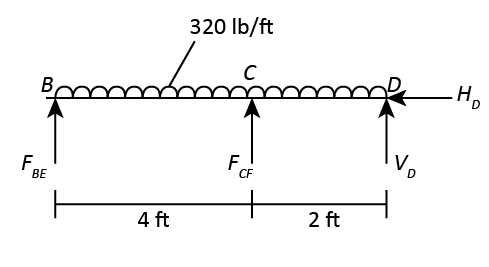
The number of unknowns in the beam is 4.
The number of available equilibrium equations is 3.
Since, the number of unknowns is more than the number of equilibrium equations, the beam is statically indeterminate.
Adopt Moment Distribution Method to solve the beam.
Calculate the Fixed End Moments.
The fixed end moments for beam subjected to uniformly distributed load is given by,
Therefore, the fixed end moments for span BC is,
The fixed end moments for span CD is,
Calculate the distributing factors for the beam spans.
|
Point |
Span |
Stiffness |
Total Stiffness |
Distribution Factor |
| C |
BC |
3EI/4=0.75EI |
2.25EI |
0.33 |
|
CD |
3EI/2=1.5EI |
0.67 |
Calculate the actual moments at the support
|
|
BC |
CB |
CD |
DC |
|
Distribution Factors |
- |
0.33 |
0.67 |
|
|
Fixed End Moments |
426.67 |
-426.67 |
106.67 |
-106.67 |
|
Adjustment of Moment at B and D |
-426.67 |
- |
- |
+106.67 |
|
Carryover Moment |
- |
-213.33 |
+53.33 |
- |
|
Total Moment |
0 |
-640 |
160 |
0 |
|
Adjustment of Moment at B and C |
0 |
+158.4 |
+321.6 |
0 |
|
Total Moment |
0 |
-481.6 |
+481.6 |
0 |
Calculate Support Reactions.
Calculate Support reaction for Span BC.
The following figure shows the Free Body Diagram of the Span BC.
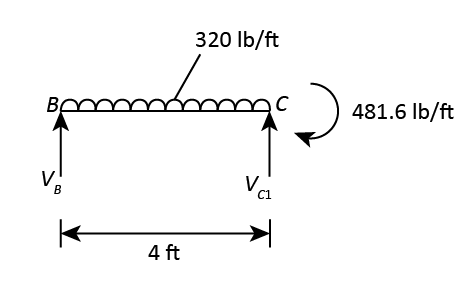
Consider moment of all the forces with respect to Point B.
Since the beam is in equilibrium, the sum of the moment at B will be zero.
The sum of all the forces in Y-direction is zero.
Calculate Support reaction for Span CD.
The following figure shows the Free Body Diagram of the Span CD.
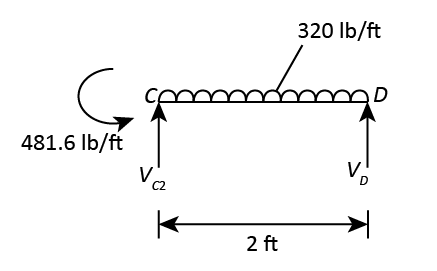
Consider moment of all the forces with respect to Point D.
Since the beam is in equilibrium, the sum of the moment at D will be zero.
The sum of all the forces in Y-direction is zero.
The sum of all the forces in X-direction is zero.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









