Determine the electrical power supplied to a boiler when the temperature of the entering water is 20 C and the exiting temperature is 89 C. The flow of.the pressured water is 2 Kg/s. There is a negligible pressure drop through this boiler and it operates at a constant pressure of 3 bars. The specific heat is c = 4,370 J/(Kg K). There is a 150W rate of heat loss from the boiler during this process to a surrounding at 293.2 k. Consider steady state conditions.Calculate the total rate of entropy production in
Determine the electrical power supplied to a boiler when the temperature of the entering water is 20 C and the exiting temperature is 89 C. The flow of.the pressured water is 2 Kg/s. There is a negligible pressure drop through this boiler and it operates at a constant pressure of 3 bars. The specific heat is c = 4,370 J/(Kg K). There is a 150W rate of heat loss from the boiler during this process to a surrounding at 293.2 k. Consider steady state conditions.
Calculate the total rate of entropy production in
The inlet and exit temperature respectively are 20 degree Celsius and 89 degree Celsius. Also, the flow rate of pressured water is 2 kg/s. Consider Q as the heat energy, m as the mass, C as the specific heat, Tf as the exit temperature, and Ti as the inlet temperature. Also, consider P as the electrical power. Now, the rate of heat energy gives power. Thus, calculate the required electrical power.
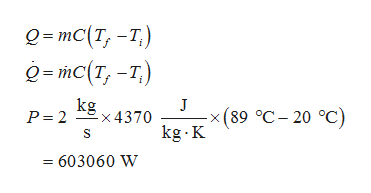
The pressure drop in the boiler is negligible. Calculate the rate of entropy when the flow raises heat in the boiler.
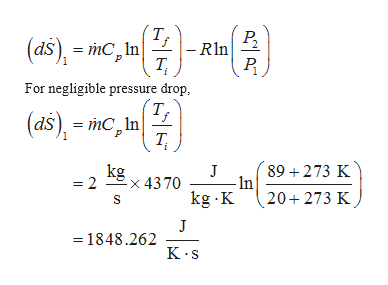
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









