1 Saturated Hydrocarbons 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 3 Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers 4 Aldehydes And Ketones 5 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, And Other Acid Derivatives 6 Amines And Amides 7 Carbohydrates 8 Lipids 9 Proteins 10 Enzymes And Vitamins 11 Nucleic Acids 12 Biochemical Energy Production 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism 14 Lipid Metabolism 15 Protein Metabolism Chapter5: Carboxylic Acids, Esters, And Other Acid Derivatives
5.1 Structure Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives 5.2 Iupac Nomenclature Of Carboxylic Acids 5.3 Common Names For Carboxylic Acids 5.4 Polyfunctional Carboxylic Acids 5.5 Physical Properties Of Carboxylic Acids 5.6 Preparation Of Carboxylic Acids 5.7 Acidity Of Carboxylic Acids 5.8 Carboxylic Acids Salts 5.9 Carboxylic Acid Decarboxylation Reactions 5.10 Structures Of Esters 5.11 Preparation Of Esters 5.12 Nomenclature For Esters 5.13 Selected Common Esters 5.14 Isomerism For Carboxylic Acids And Esters 5.15 Physical Properties Of Esters 5.16 Chemical Properties Of Esters 5.17 Sulfur Analogs Of Esters 5.18 Polyesters 5.19 Acid Chlorides And Acid Anhydrides 5.20 Esters And Anhydrides Of Inorganic Acids Chapter Questions Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.1EP Problem 5.2EP Problem 5.3EP Problem 5.4EP: Indicate whether or not each of the compounds in Problem 16-2 is a carboxylic acid. Problem 5.5EP Problem 5.6EP Problem 5.7EP Problem 5.8EP Problem 5.9EP Problem 5.10EP Problem 5.11EP Problem 5.12EP Problem 5.13EP Problem 5.14EP Problem 5.15EP Problem 5.16EP: Assign an IUPAC name to each of the following carboxylic acids. Problem 5.17EP Problem 5.18EP Problem 5.19EP Problem 5.20EP Problem 5.21EP Problem 5.22EP Problem 5.23EP Problem 5.24EP Problem 5.25EP Problem 5.26EP Problem 5.27EP Problem 5.28EP Problem 5.29EP Problem 5.30EP Problem 5.31EP Problem 5.32EP Problem 5.33EP Problem 5.34EP Problem 5.35EP Problem 5.36EP Problem 5.37EP Problem 5.38EP Problem 5.39EP Problem 5.40EP Problem 5.41EP: Determine the maximum number of hydrogen bonds that can form between an acetic acid molecule and a.... Problem 5.42EP Problem 5.43EP Problem 5.44EP Problem 5.45EP Problem 5.46EP Problem 5.47EP Problem 5.48EP Problem 5.49EP Problem 5.50EP Problem 5.51EP Problem 5.52EP Problem 5.53EP Problem 5.54EP Problem 5.55EP: Draw structural formulas for the following entities. a. Propanoate ion b. Sodium propanoate c.... Problem 5.56EP Problem 5.57EP: Give the IUPAC name for each of the following carboxylic acid salts. Problem 5.58EP: Give the IUPAC name for each of the following carboxylic acid salts. Problem 5.59EP Problem 5.60EP Problem 5.61EP Problem 5.62EP Problem 5.63EP Problem 5.64EP Problem 5.65EP Problem 5.66EP: Which three carboxylic acids have salts that are used extensively as food preservatives? Problem 5.67EP Problem 5.68EP: Which carboxylic acid has salts that are used to inhibit yeast and mold growth in the following? a.... Problem 5.69EP Problem 5.70EP Problem 5.71EP Problem 5.72EP Problem 5.73EP Problem 5.74EP Problem 5.75EP Problem 5.76EP Problem 5.77EP Problem 5.78EP Problem 5.79EP Problem 5.80EP Problem 5.81EP Problem 5.82EP Problem 5.83EP Problem 5.84EP Problem 5.85EP Problem 5.86EP Problem 5.87EP Problem 5.88EP Problem 5.89EP Problem 5.90EP Problem 5.91EP: Assign common names to each of the esters in Problem 16-89. Problem 5.92EP Problem 5.93EP Problem 5.94EP: Assign an IUPAC name to each of the following esters. Problem 5.95EP: Draw a structural formula for each of the following esters. a. Methyl formate b. Ethyl phenylacetate... Problem 5.96EP Problem 5.97EP Problem 5.98EP Problem 5.99EP Problem 5.100EP Problem 5.101EP Problem 5.102EP: How many carbon atoms are present in a molecule of each of the compounds in Problem 16-100? a. Ethyl... Problem 5.103EP Problem 5.104EP Problem 5.105EP Problem 5.106EP Problem 5.107EP Problem 5.108EP Problem 5.109EP Problem 5.110EP Problem 5.111EP Problem 5.112EP Problem 5.113EP Problem 5.114EP Problem 5.115EP Problem 5.116EP Problem 5.117EP Problem 5.118EP Problem 5.119EP Problem 5.120EP Problem 5.121EP Problem 5.122EP Problem 5.123EP Problem 5.124EP Problem 5.125EP: Write the structural formulas of the reaction products when each of the following esters is... Problem 5.126EP Problem 5.127EP Problem 5.128EP Problem 5.129EP Problem 5.130EP Problem 5.131EP Problem 5.132EP Problem 5.133EP Problem 5.134EP Problem 5.135EP Problem 5.136EP Problem 5.137EP Problem 5.138EP Problem 5.139EP Problem 5.140EP Problem 5.141EP Problem 5.142EP Problem 5.143EP Problem 5.144EP Problem 5.145EP Problem 5.146EP Problem 5.147EP Problem 5.148EP Problem 5.149EP: Draw a condensed structural formula for the organic product of the reaction of each of the following... Problem 5.150EP: Draw a condensed structural formula for the organic product of the reaction of each of the following... Problem 5.151EP Problem 5.152EP Problem 5.153EP Problem 5.154EP Problem 5.155EP Problem 5.156EP Problem 5.157EP Problem 5.158EP Problem 5.159EP Problem 5.160EP Problem 5.161EP Problem 5.162EP Problem 5.163EP Problem 5.164EP Problem 5.155EP
Related questions
Define the Oxidation of the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid ?
Definition Definition Class of organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group ( - COOH ) and has a general formula R - COOH or R - CO 2 H , where R refers to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other groups. They can undergo different chemical reactions, such as acid-base reactions, esterification, and oxidation. These are essential components of living organisms, playing important roles in metabolic processes, signaling, and as pharmaceuticals.
Expert Solution
Oxidation : It is the phenomenon where there is a gain of oxygen atom by the compound. In terms of electrons, oxidation is the phenomenon where there is the loss of electrons from the compound. In terms of hydrogen, oxidation is the phenomenon where there is the loss of hydrogen from the compound.
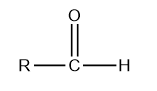
The general structure of aldehyde is given below:
Where R is alkyl or aryl group.
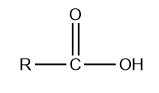
The general structure of carboxylic acid is given below:
Where R is alkyl or aryl group.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
UNLOCK THE REST