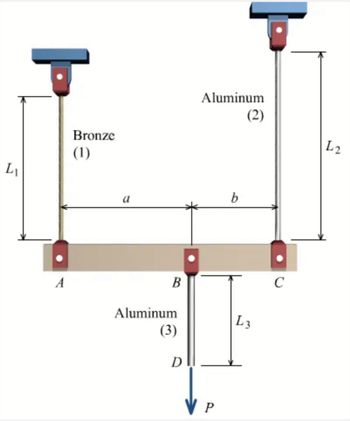
Rigid bar ABC is supported by bronze rod (1) and aluminum rod (2), as shown. A concentrated load P is applied to the free end of aluminum rod (3). Bronze rod (1) has an elastic modulus of E1 = 15,000 ksi and a diameter of d1 = 0.50 in. Aluminum rod (2) has an elastic modulus of E2 = 10,000 ksi and a diameter of d2 = 0.85in. Aluminum rod (3) has a diameter of d3 = 1.00in. The yield strength of the bronze is 48 ksi and the yield strength of the aluminum is 40 ksi. Assume a = 2.5 ft, b = 1.5 ft, L1 = 6 ft, L2 = 8 ft, and L3 = 3 ft. (A) Calculate the cross-sectional areas of the three rods. in in.2 (B) For a factor of safety of 2.1, calculate the allowable stresses in the bronze and the aluminum rods. IN KSI. (C) What is the magnitude of load P that can safely be applied to the structure for a minimum factor of safety of 2.1? in kips (D) The pin used at B has an ultimate shear strength of 58 ksi. If a factor of safety of 2.5 is required, determine the allowable shear stress in this pin. in ksi (E) The pin used at B is a double shear pin connection. Determine the minimum pin cross-sectional area, and the corresponding minimum pin diameter that can be used at B. (Amin IN in.2 and dpin IN in.)
Rigid bar ABC is supported by bronze rod (1) and aluminum rod (2), as shown. A concentrated load P is applied to the free end of aluminum rod (3). Bronze rod (1) has an elastic modulus of E1 = 15,000 ksi and a diameter of d1 = 0.50 in. Aluminum rod (2) has an elastic modulus of E2 = 10,000 ksi and a diameter of d2 = 0.85in. Aluminum rod (3) has a diameter of d3 = 1.00in. The yield strength of the bronze is 48 ksi and the yield strength of the aluminum is 40 ksi. Assume a = 2.5 ft, b = 1.5 ft, L1 = 6 ft, L2 = 8 ft, and L3 = 3 ft.
(A) Calculate the cross-sectional areas of the three rods. in in.2
(B) For a factor of safety of 2.1, calculate the allowable stresses in the bronze and the aluminum rods. IN KSI.
(C) What is the magnitude of load P that can safely be applied to the structure for a minimum factor of safety of 2.1? in kips
(D) The pin used at B has an ultimate shear strength of 58 ksi. If a factor of safety of 2.5 is required, determine the allowable shear stress in this pin. in ksi
(E) The pin used at B is a double shear pin connection. Determine the minimum pin cross-sectional area, and the corresponding minimum pin diameter that can be used at B. (Amin IN in.2 and dpin IN in.)

Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 9 images

(G) Using these results (δ1=0.1097 in. , δ2=0.1265 in. , δ3=0.0548 in.) determine the deflections of Joint B and Point D. ANSWERS in inch
(H) On a piece of paper, sketch a free body diagram (FBD) cut through rod (3) and also a FBD of the rigid bar. Using these, find a relationship between the force in rod 1 (F1) and the applied load, P, a relationship between the force in rod 2 (F2) and the applied load, P, and also a relationship between the force in rod 3 (F3) and the applied load, P.
(I) Based on the allowable stress for the bronze, calculate the maximum allowable force that can be supported by rod (1), and the corresponding maximum value for the applied load P. IN KIPS
(J) Based on the allowable stress for the aluminum, calculate the maximum allowable force that can be supported by rod (2) and rod 3, and the corresponding maximum value for the applied load P. IN KIPS
(K) Using the results from Part 8, determine the deflections of Joint B and Point D. IN INCH
NOTE: These are the last part. pls, answer. thanks!
(D) The pin used at B has an ultimate shear strength of 58 ksi. If a factor of safety of 2.5 is required, determine the allowable shear stress in this pin. in ksi
(E) The pin used at B is a double shear pin connection. Determine the minimum pin cross-sectional area, and the corresponding minimum pin diameter that can be used at B. (Amin IN in.2 and dpin IN in.)
(F) Determine the deformations in rods (1), (2), and (3) when load P equals Pmax from Letter C. ANSWERS in inch
(G) Using the results from Letter F, determine the deflections of Joint B and Point D. ANSWERS in inch








