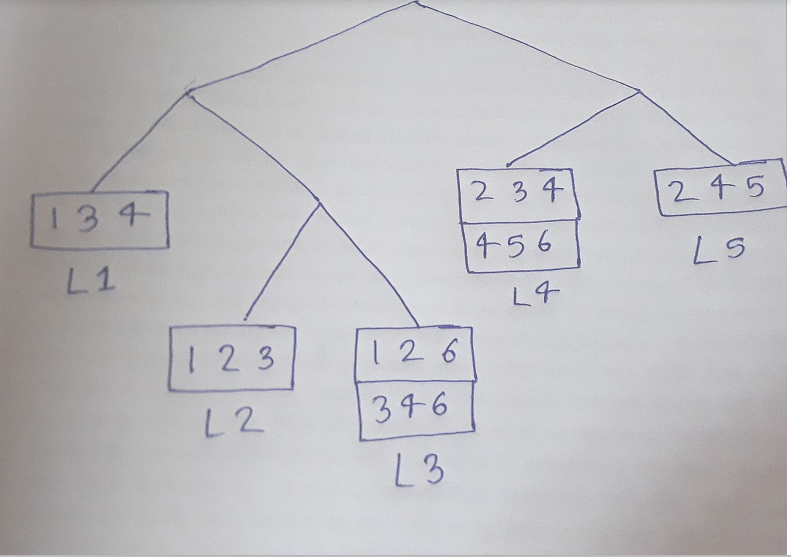
Consider the following set of candidate 3-itemsets: {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 6}, {1, 3, 4}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 5, 6} Consider a transaction that contains the following items: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}. Using the hash tree constructed how do we decide which leaf nodes will be checked against the transaction? What are the candidate 3-itemsets contained in the transaction? Construct a hash tree for the above candidate 3-itemsets. Assume the tree uses a hash function where all odd-numbered items are hashed to the left child of a node, while the even-numbered items are hashed to the right child. A candidate k-itemset is inserted into the tree by hashing on each successive item in the candidate and then following the appropriate branch of the tree according to the hash value. Once a leaf node is reached, the candidate is inserted based on one of the following conditions: Condition 1: If the depth of the leaf node is equal to k (the root is assumed to be at depth 0), then the candidate is inserted regardless of the number of itemsets already stored at the node. Condition 2: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k, then the candidate can be inserted as long as the number of itemsets stored at the node is less than maxsize. Assume maxsize = 2 for this question. Condition 3: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k and the number of itemsets stored at the node is equal to maxsize, then the leaf node is converted into an internal node. New leaf nodes are created as children of the old leaf node. Candidate itemsets previously stored in the old leaf node are distributed to the children based on their hash values. The new candidate is also hashed to its appropriate leaf node.
Consider the following set of candidate 3-itemsets: {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 6}, {1, 3, 4}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 5, 6} Consider a transaction that contains the following items: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}. Using the hash tree constructed how do we decide which leaf nodes will be checked against the transaction? What are the candidate 3-itemsets contained in the transaction? Construct a hash tree for the above candidate 3-itemsets. Assume the tree uses a hash function where all odd-numbered items are hashed to the left child of a node, while the even-numbered items are hashed to the right child. A candidate k-itemset is inserted into the tree by hashing on each successive item in the candidate and then following the appropriate branch of the tree according to the hash value. Once a leaf node is reached, the candidate is inserted based on one of the following conditions: Condition 1: If the depth of the leaf node is equal to k (the root is assumed to be at depth 0), then the candidate is inserted regardless of the number of itemsets already stored at the node. Condition 2: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k, then the candidate can be inserted as long as the number of itemsets stored at the node is less than maxsize. Assume maxsize = 2 for this question. Condition 3: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k and the number of itemsets stored at the node is equal to maxsize, then the leaf node is converted into an internal node. New leaf nodes are created as children of the old leaf node. Candidate itemsets previously stored in the old leaf node are distributed to the children based on their hash values. The new candidate is also hashed to its appropriate leaf node.
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
Consider the following set of candidate 3-itemsets: {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 6}, {1, 3, 4}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 5, 6}
Consider a transaction that contains the following items: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}. Using the hash tree constructed how do we decide which leaf nodes will be checked against the transaction? What are the candidate 3-itemsets contained in the transaction?
Construct a hash tree for the above candidate 3-itemsets. Assume the tree uses a hash function where all odd-numbered items are hashed to the left child of a node, while the even-numbered items are hashed to the right child. A candidate k-itemset is inserted into the tree by hashing on each successive item in the candidate and then following the appropriate branch of the tree according to the hash value. Once a leaf node is reached, the candidate is inserted based on one of the following conditions:
Condition 1: If the depth of the leaf node is equal to k (the root is assumed to be at depth 0), then the candidate is inserted regardless of the number of itemsets already stored at the node.
Condition 2: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k, then the candidate can be inserted as long as the number of itemsets stored at the node is less than maxsize. Assume maxsize = 2 for this question.
Condition 3: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k and the number of itemsets stored at the node is equal to maxsize, then the leaf node is converted into an internal node. New leaf nodes are created as children of the old leaf node. Candidate itemsets previously stored in the old leaf node are distributed to the children based on their hash values. The new candidate is also hashed to its appropriate leaf node.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Hash Tree Problem
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY