Consider an ideal refrigeration cycle which use R-134 a as the working fluid. The temperature of the refrigerant in the evaporator is -10oC and in the condenser is 36oC. If the refrigerant flow rate is 0.5 kg/s, please calculate COP (coefficient of performance) and the plant cooling capacity?
Consider an ideal refrigeration cycle which use R-134 a as the working fluid. The temperature of the refrigerant in the evaporator is -10oC and in the condenser is 36oC. If the refrigerant flow rate is 0.5 kg/s, please calculate COP (coefficient of performance) and the plant cooling capacity?
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Consider an ideal refrigeration cycle which use R-134 a as the working fluid. The temperature of the refrigerant in the evaporator is -10oC and in the condenser is 36oC. If the refrigerant flow rate is 0.5 kg/s, please calculate COP (coefficient of performance) and the plant cooling capacity?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Which R134a table is referring to? My reference as attached. The answer result should be different?
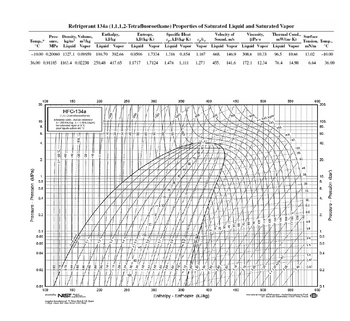
Transcribed Image Text:Pression (MPa)
Pressure
Pres- Density, Volume,
Temp., sure, kg/m³ m³/kg
MPa Liquid Vapor Liquid Vapor Liquid Vapor
-10.00 0.20060 1327.1 0.09959 186.70 392.66 0.9506 1.7334
36.00 0.91185 1163.4 0.02238 250.48 417.65 1.1717 1.7124 1.476 1.111
100
20.
10.
8.
6.
4.
2.
1.
0.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.1
0.08
0.06
0.04
0.02
0.01
Refrigerant 134a (1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane)
Entropy,
kJ/(kg-K)
150
HFC-134a
(1,1,124)
fence sedere
2000 kg; s=1.00 K)
forcatura queda
pour quidescu 0°C
3 2/2 2/2
100
pely NIST
2. Pye Laver Not Diana 201
M
150
Enthalpy,
kJ/kg
--00
200
200
250
819-8-18
250
Properties of Saturated Liquid and Saturated Vapor
Velocity of Viscosity, Thermal Cond
Sound, m/s
Pa's
Specific Heat
Surface
p. kJ/(kg-K) plc.
mW/(mK)
Tension, Temp..
Liquid Vapor Vapor Liquid Vapor Liquid Vapor Liquid Vapor mN/m °C
306.6 10.33
172.1 12.34
1.316 0.854 1.167
1.273
668. 146.9
455. 141.6
96.5 10.66 13.02 -10,00
76.4 14.98
6,64 36.00
300
300
350
400
XNXX
350
Enthalpy - Enthalpie (kJ/kg)
400
450
450
-60%
28
500
= 500 kg/m²
400L
100
300.
UN
LONE
JOKO KI
560
200
09
•DPI+'
is.
EN
BUST
-1-160
550
88/8
40.
SITR
18-42
#T
F
30.
4
+ Pe
20
15.
10.
8.0
60
40
IN
T
++
30
2.0
1.5
M
1.0
-0.80
0,60
500
Inteligente Angered
177, Ves, Fal/Tr
6:00
200.
100.
80.
60.
599
40.
20.
10.
8.
6,
4.
1.
0.8
0.8
0,4
0.2
0.1
6:00
Pressure Pression (bar)
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY