Consider a population of 250 with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation equal to 22. What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50? Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table. Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table Cumulative probability to the left of z (page 1) What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50? P(xs53) (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Table entries represent the shaded area in the figure Cumulative probability FIRST DIGIT OF Zz SECOND DIGIT OF z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 005 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 -3.0 0.0013 0.0013 0.0013 0.0012 0.0012 0.0011 0.0011 0.0011 0.0010 0.0010 -2.9 0.0019 0.0018 0.0018 0.0017 0.0016 0.0016 0.0015 0.0015 0.0014 0.0014 -28 0.0026 0.0025 0.0024 0.0023 0.0023 0.0022 0.0021 0.0021 0.0020 0.0019 -2.7 0.0035 0.0034 0.0033 0.0032 0.0031 0.0030 0.0029 0.0028 0.0027 0.0026 -2.6 0.0047 0.0045 0.0044 0.0043 0.0041 0.0040 0.0039 0.0038 0.0037 0.0036 -25 0.0062 0.0060 0.0059 0.0057 0.0055 0.0054 0.0052 0.0051 0.0049 0.0048 -24 0.0082 0.0080 0.0078 0.0075 0.0073 0.0071 0.0069 0.0068 0.0066 0.0064 -23 0.0107 0.0104 0.0102 0.0099 0.0096 0.0094 0.0091 0.0089 0.0087 0.0084 -2.2 0.0139 0.0136 0.0132 0.0129 0.0125 0.0122 0.0119 0.0116 0.01 13 0.01 10 -2.1 0.0179 0.0174 0.01 70 0.0166 0.0162 0.0158 0.0154 0.0150 0.0146 0.0143 -20 0.0228 0.0222 0.0217 0.0212 0.0207 0.0202 0.0197 0.0192 0.0188 0.0183 -19 0.0287 00281 0.0274 0.0268 0.0262 0.0256 0.0250 0.0244 0.0239 0.0233 -18 0.0359 0.0351 0.0344 0.0336 0.0329 0.0322 0.0314 0.0307 0.0301 0.0294 -1.7 0.0446 0.0436 0.0427 0.0418 0.0409 0.0401 0.0392 0.0384 0.0375 0.0367 -1.6 0.0548 0.0537 0.0526 0.0516 0.0505 0.0495 0.0485 0.0475 0.0465 0.0455 -15 0.0668 0.0655 0.0643 0.0630 0.0618 0.0606 0.0594 0.0582 0.0571 0.0559 -14 0.0808 0.0793 0.0778 0.0764 0.0749 0.0735 0.0721 0.0708 0.0694 0.0681 -13 0.0968 0.0951 0.0934 0.0918 0.0901 0.0885 0.0838 0.0869 0.0853 0.0823 -12 0.1151 0.1131 0.1112 0.1093 0.1075 0.1056 0.1038 0.1020 0.1003 0.0985 -11 0.1357 0.1335 0.1314 O1202 0.1292 0.1271 0.1251 0.1230 0.1210 0.1190 0.1170 -1.0 0.1587 0.1562 0.1539 0.1515 0.1492 0.1469 0.1446 0.1423 0.1401 0.1379 -0.9 0.1841 0.1814 0.1788 0.1762 0.1736 0.1711 0.1685 0.1660 0.1635 0.1611 -0.8 02119 0.2090 02389 0.2061 0.2033 0.2005 0.1977 0.1949 0.1922 0.1894 0.1867 -0.7 0.2420 0.2358 0.2327 0.2296 0.2266 0.2236 0.2206 0.2177 02148
Consider a population of 250 with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation equal to 22. What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50? Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table. Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table Cumulative probability to the left of z (page 1) What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50? P(xs53) (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Table entries represent the shaded area in the figure Cumulative probability FIRST DIGIT OF Zz SECOND DIGIT OF z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 005 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 -3.0 0.0013 0.0013 0.0013 0.0012 0.0012 0.0011 0.0011 0.0011 0.0010 0.0010 -2.9 0.0019 0.0018 0.0018 0.0017 0.0016 0.0016 0.0015 0.0015 0.0014 0.0014 -28 0.0026 0.0025 0.0024 0.0023 0.0023 0.0022 0.0021 0.0021 0.0020 0.0019 -2.7 0.0035 0.0034 0.0033 0.0032 0.0031 0.0030 0.0029 0.0028 0.0027 0.0026 -2.6 0.0047 0.0045 0.0044 0.0043 0.0041 0.0040 0.0039 0.0038 0.0037 0.0036 -25 0.0062 0.0060 0.0059 0.0057 0.0055 0.0054 0.0052 0.0051 0.0049 0.0048 -24 0.0082 0.0080 0.0078 0.0075 0.0073 0.0071 0.0069 0.0068 0.0066 0.0064 -23 0.0107 0.0104 0.0102 0.0099 0.0096 0.0094 0.0091 0.0089 0.0087 0.0084 -2.2 0.0139 0.0136 0.0132 0.0129 0.0125 0.0122 0.0119 0.0116 0.01 13 0.01 10 -2.1 0.0179 0.0174 0.01 70 0.0166 0.0162 0.0158 0.0154 0.0150 0.0146 0.0143 -20 0.0228 0.0222 0.0217 0.0212 0.0207 0.0202 0.0197 0.0192 0.0188 0.0183 -19 0.0287 00281 0.0274 0.0268 0.0262 0.0256 0.0250 0.0244 0.0239 0.0233 -18 0.0359 0.0351 0.0344 0.0336 0.0329 0.0322 0.0314 0.0307 0.0301 0.0294 -1.7 0.0446 0.0436 0.0427 0.0418 0.0409 0.0401 0.0392 0.0384 0.0375 0.0367 -1.6 0.0548 0.0537 0.0526 0.0516 0.0505 0.0495 0.0485 0.0475 0.0465 0.0455 -15 0.0668 0.0655 0.0643 0.0630 0.0618 0.0606 0.0594 0.0582 0.0571 0.0559 -14 0.0808 0.0793 0.0778 0.0764 0.0749 0.0735 0.0721 0.0708 0.0694 0.0681 -13 0.0968 0.0951 0.0934 0.0918 0.0901 0.0885 0.0838 0.0869 0.0853 0.0823 -12 0.1151 0.1131 0.1112 0.1093 0.1075 0.1056 0.1038 0.1020 0.1003 0.0985 -11 0.1357 0.1335 0.1314 O1202 0.1292 0.1271 0.1251 0.1230 0.1210 0.1190 0.1170 -1.0 0.1587 0.1562 0.1539 0.1515 0.1492 0.1469 0.1446 0.1423 0.1401 0.1379 -0.9 0.1841 0.1814 0.1788 0.1762 0.1736 0.1711 0.1685 0.1660 0.1635 0.1611 -0.8 02119 0.2090 02389 0.2061 0.2033 0.2005 0.1977 0.1949 0.1922 0.1894 0.1867 -0.7 0.2420 0.2358 0.2327 0.2296 0.2266 0.2236 0.2206 0.2177 02148
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
What is probably of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50?
**Round to four decimal places as needed**

Transcribed Image Text:Consider a population of 250 with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation equal to 22. What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50?
Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table.
Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table
Cumulative probability to the left of z (page 1)
What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50?
P(xs 53) =
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Cumulative
Table entries
probability
popeus oq uasaadar
area in the figure
FIRST DIGIT OF z
SECOND DIGIT OF z
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
-3.0
0.0013
0.0013
0.0013
0.0012
0.0012
0.0011
0.0011
0.001I
0.0010
0.0010
-2.9
0.0019
0.0018
0.0018
0.0017
0.0016
0.0016
0.0015
0.0015
0.0014
0.0014
-2.8
0.0026
0.0025
0.0024
0.0023
0.0023
0.0022
0,0021
0.0021
0.0020
0.0019
-2.7
0.0035
0.0034
0.0033
0.0032
0.0031
0.0030
0.0029
0.0028
0.0027
0.0026
2.6
0.0047
0.0045
0.0044
0.0043
0.0041
0.0040
0.0039
0.0038
0.0037
0.0036
-2.5
0.0062
0.0060
0.0059
0.0057
0.0055
0.0054
0.0052
0.0051
0.0049
0.0048
-24
0.0082
0.0080
0.0078
0.0075
0.0073
0.0071
0.0069
0.0068
0.0066
0.0064
+2.3
0.0107
0.0104
0.0102
0.0099
0.0096
0.0094
0.0091
0.0089
0.0087
0.0084
-2.2
0.0139
0.0136
0.0132
0.0129
0.0125
0.0122
0.0119
0.0116
0.01 13
0.01 10
-2.1
0.0179
0.0174
0.01 70
0.0166
0.0162
0.0158
0.0154
0.0150
0.0146
0.0143
-2.0
0.0228
0.0222
0.0217
0.0212
0.0207
0.0202
0.0197
0.0192
0.0188
0.0183
-1.9
0.0287
0.0281
0.0274
0.0268
0.0262
0.0256
0.0250
0.0244
0.0239
0.0233
-1.8
0.0359
0.0351
0.0344
0.0336
0.0329
0.0322
0.0314
0.0307
0.0301
0.0294
-1.7
0.0446
0.0436
0.0427
0.0418
0.0409
0.0401
0.0392
0.0384
0.0375
0.0367
-1.6
0.0548
0.0537
0.0526
0.0516
0.0505
0.0495
0.0485
0.0475
0.0465
0.0455
-1.5
0.0668
0.0655
0.0643
0.0630
0.0618
0.0606
0.0594
0.0582
0.0571
0.0559
-14
0.0808
0.0793
0.0778
0.0764
0.0749
0.0735
0.0721
0.0708
0.0694
0.0681
-13
0.0968
0.0951
0.0934
0.0918
0.0901
0.0885
0.0869
0.0853
0.0838
0.0823
-1.2
0.1151
0.1131
0.1112
0.1093
0.1075
0.1056
0.1038
0.1020
0.1003
0.0985
-1.1
0.1357
0.1335
0.1314
0.1292
0.1271
0.1251
0,1230
0.1210
0.1190
0.1170
-1.0
0.1587
0.1562
0.1539
0.1515
0.1492
0.1469
0.1446
0.1423
0.1401
0.1379
-0.9
0.1841
0.1814
0.1788
0.1762
0.1736
0.1711
0.1685
0.1660
0.1635
0.1611
-0.8
0.2119
0.2090
0.2061
0.2033
0.2005
0.1977
0.1949
0.1922
0.1894
0.1867
-0.7
0.2420
0.2389
0.2358
0.2327
0.2296
0.2266
0.2236
0.2206
0.2177
02148

Transcribed Image Text:Consider a population of 250 with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation equal to 22. What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50?
Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table
Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table.
Cumulative probability to the left of z (page 2)
What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean of 53 or less from a sample of 50?
P(xs53)
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Cumulative
probebility
Table entries
represent the shaded
Area in the figure
FIRST DIGIT OF z
SECOND DIGIT OFz
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
0,0
05000
0.5040
0.5080
0.5120 05160 05199
0.5239
0.5279
05319
0.5359
0.1
0.5398
0.5438
0.5478
0.5517
0.5557
0.596
0.5636
0.5675
05714
0.5753
0.2
05793
0.5832 0.587I
0.5910
0.5948
0.5987
0.6026
0.6064
0.6103
0.6141
0.3
0.61 79
0.6217
0.6255 0,6293
0.6331
0.6368
0.6406
0.6443
0.6480
06517
0.4
0.6554
0.6591
0.6628
0.6664
0.6700
06736
0.6772
0.6808
0.6844
0.6879
0.5
0.6915
0.6950
0.6985
0.7019
0,7054
0,7088
0.7123
0.7157
0.7190
0.7224
0.6
0.7257
0.7291 0,7324
0.7357
0.7389
0,7422
0.7454
0.7486
0.7517
0.7549
0.7
0.7580
0.7611
0.7642
0.7673 0.7704
0.7734
0.7764
0.7794
0.7823
0.7852
0.8
0.7881
0,7910
0,7939
0.7967
0.7995
0.8023
0.8051
0.8078
0.8106
0.8133
0.9
0.8159
0.8186
0,8212
0.8238
0.8264
0.8289
O8280
0.8315
0.8340
08365
0.8389
1.0
0.8413
0,8438
0.8461
0.8485
0.8508
0.8531
0.8554
0.8577
08599
0.8621
11
0.8643
0.8665
0.8686
0.8708
0.8729
0.8749
0.8770
0.8790
0.8810
0.8830
1.2
0.8849
0.8869
0.8888
80.8907
0.8925
0.8944
0.8962
0.8980
08997
0.9015
1.3
0.9032
0.9049
0.9066
0.9082
0.0000
0,9099
0.9115
0.9131
0.9147
0.9162
09177
14
0.9192
0.9207 0.9222
0.9236
0.9251
0.9265
0.9279
0.9292
0.9306
0.9319
1.5
0.9332 0.9345
0.9357
0.9370
0.9382
0.9394
0.9406
0.9418
0.9429
0.9441
1.6
0.9484 0.9505
0.9452
0.9463 0.9474
0.9495
09515
0.9525
0.9535
0.9545
1.7
0.9554
00564 0.9573
0.9582
0,9591
09599
0.9608
0.9616
0.9625
0.9633
1.8
0.9641
0.9640 0.9656
0.9664
0.9671
0.9678
0.9686
0.9693
0.9699
0.9706
1.9
0.9713
0.9719 09726
0.9732
0.9738
0.9744
0.9750
0.9756
0.9761
0.9767
2.0
0.9772
0.9778
0.9783
0.9788
0.9793
0.9798
0.9803
0.9808
0.9812
0.9817
21
0.9821
0.9826
0.9830
0.9834
0.9838
0.9842
0.9846
0.9850
0.9854
0.9857
22
0.9861
0.9864
0.9868
0.9871
0.9875
0.9878
0.9881
0.9884
0.9887
0.9890
23
0.9893
09896
0.9898
0.9901
0.9904
0.9906
0.9909
0.9911
0.9913
0.9916
Expert Solution
Step 1
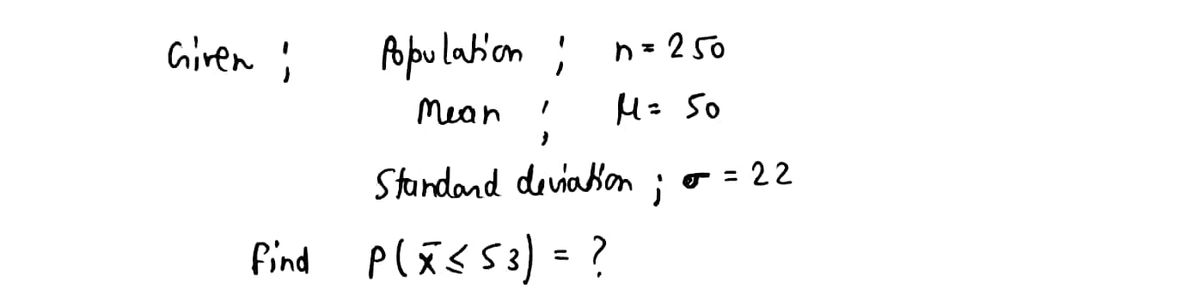
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman