Consider a box of length 2L, where L = 1 m. The bowstring is made up of two cords of natural length 1 m meeting in the center, each with stiffness 127 N/m. An archer pulls back the string a distance 0.31 m. What would be the force on an arrow in this state, in N? (Note: There are two cords and their vertical components of their elastic forces will cancel, see below.)
Consider a box of length 2L, where L = 1 m. The bowstring is made up of two cords of natural length 1 m meeting in the center, each with stiffness 127 N/m. An archer pulls back the string a distance 0.31 m. What would be the force on an arrow in this state, in N? (Note: There are two cords and their vertical components of their elastic forces will cancel, see below.)
Related questions
Question
Consider a box of length 2L, where L = 1 m. The bowstring is made up of two cords of natural length 1 m meeting in the center, each with stiffness 127 N/m. An archer pulls back the string a distance 0.31 m. What would be the force on an arrow in this state, in N? (Note: There are two cords and their vertical components of their elastic forces will cancel, see below.)
(Please answer to the fourth decimal place - i.e 10.5432)

Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates the transformation of a lens into a geometric shape, possibly a cone.
- On the left, there is an outline of a concave lens depicted with dashed lines, suggesting its initial form.
- An arrow pointing to the right indicates the directional transformation or projection process towards the next shape.
- On the right, there is a geometric representation resembling a cone with dashed lines outlining its form. The shape has a height labeled as "2L" and a width at the base labeled as "x."
This diagram could be used to describe a process in optics or geometric transformation, possibly explaining how light or images are projected through lenses to form specific shapes.
Expert Solution
Step 1
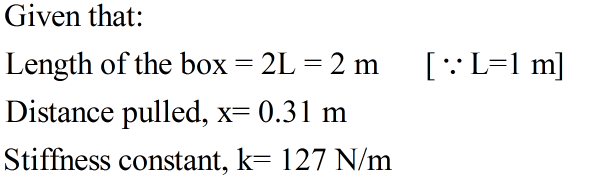
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
