DNA and RNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is usually called the blueprint of life. Deoxyribose is a monosaccharide that has a key function in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. One less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group occurs in deoxyribose sugar. Nucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid, is one of the natural components. Deoxyribonucleic acid is a double-stranded molecule. Watson and Crick postulated the double-stranded model of the helix. A deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecular group that carries and transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. All eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are involved.
DNA as the Genetic Material
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a long polymeric nucleic acid molecule discovered in the late 1930s. It is a polymer; a long chain-like molecule made up of several monomers connected in a sequence. It possesses certain characteristics that qualify it as a genetic component. Certain organisms have different types of nucleic acids as their genetic material - DNA or RNA.
Genetics
The significant branch in science which involves the study of genes, gene variations, and the organism's heredity is known as genetics. It is also used to study the involvement of a gene or set of genes in the health of an individual and how it prevents several diseases in a human being. Thus, genetics also creates an understanding of various medical conditions.
DNA Replication
The mechanism by which deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is capable of producing an exact copy of its own is defined as DNA replication. The DNA molecules utilize a semiconservative method for replication.
Concerning the nitrogen- containing bases that participate in
All living organisms store their genetic information in form of DNA / RNA.
This genetic information is present in the nucleus of a cell and is responsible for passing the traits from parents to offspring and for coding proteins necessary for bodily functions.
DNA is made of units called as nucleotide. Each Nucleotide is made of 3 molecules – deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogen base.
These nitrogen bases in DNA/RNA are classified into 2 groups based on their chemical structure.
These 2 groups are – pyrimidines and purines.
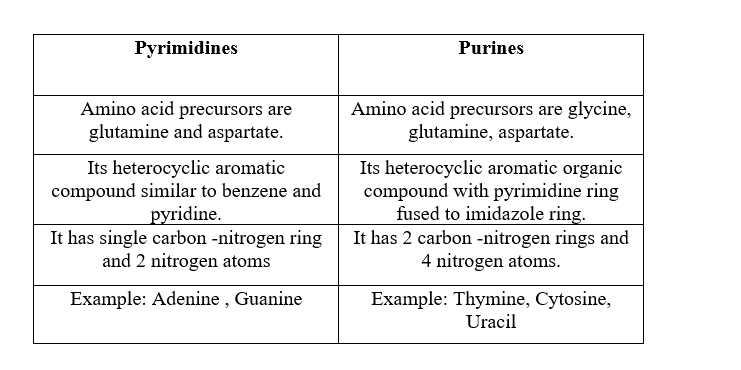
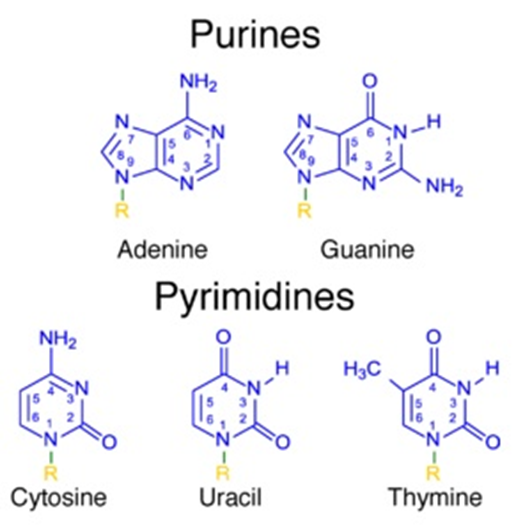
Purines and pyrimidine bases are complementary to each other.
Guanine pairs with Cytosine forming 3 hydrogen bonds.
Adenine pairs with Thymine forming 2 hydrogen bonds (In case of RNA Uracil replaces Thymine).
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









