Circuit in phone charger. Resistor can only dissipate up to 0.30 Watts of power before melting. When charger is operating normally, resistor typically has voltage of 4.2 V across, and dissipates only 0.10 Watts of power. a) What is the resistance of this resistor? b) How much current does it normally carry? c) What is the max voltage you can put across it before it overheats and melts?
Circuit in phone charger. Resistor can only dissipate up to 0.30 Watts of power before melting. When charger is operating normally, resistor typically has voltage of 4.2 V across, and dissipates only 0.10 Watts of power. a) What is the resistance of this resistor? b) How much current does it normally carry? c) What is the max voltage you can put across it before it overheats and melts?
Related questions
Question
Circuit in phone charger. Resistor can only dissipate up to 0.30 Watts of power before melting.
When charger is operating normally, resistor typically has voltage of 4.2 V across, and dissipates only 0.10 Watts of power.
a) What is the resistance of this resistor?
b) How much current does it normally carry?
c) What is the max voltage you can put across it before it overheats and melts?
Expert Solution
Step 1
The power dissipated by the resistor is related to the resistance (R) and the voltage across the capacitor (V) as below,
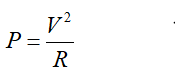
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
