Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide with hydrochloric acid, HCI(aq), as described by the chemical equation MnO,(s) + 4 HCl(aq) → MNCI, (aq) + 2 H,O(1) + Cl,(g) How much MnO, (s) should be added to excess HCl(aq) to obtain 105 mL of Cl,(g) at 25 °C and 715 Torr? (Hint: It's another stoichiometry problem. See hints for previous problems. You will get n which is moles of chlorine gas first, then use stoichiometry to get moles of the reactant that you need, then grams of that reactant.) g MnO, mass:
Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide with hydrochloric acid, HCI(aq), as described by the chemical equation MnO,(s) + 4 HCl(aq) → MNCI, (aq) + 2 H,O(1) + Cl,(g) How much MnO, (s) should be added to excess HCl(aq) to obtain 105 mL of Cl,(g) at 25 °C and 715 Torr? (Hint: It's another stoichiometry problem. See hints for previous problems. You will get n which is moles of chlorine gas first, then use stoichiometry to get moles of the reactant that you need, then grams of that reactant.) g MnO, mass:
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
![**Stoichiometry Problem: Preparing Chlorine in the Laboratory**
Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide (\( \text{MnO}_2 \)) with hydrochloric acid (\( \text{HCl(aq)} \)), as described by the chemical equation:
\[ \text{MnO}_2(s) + 4 \text{HCl(aq)} \rightarrow \text{MnCl}_2(aq) + 2 \text{H}_2\text{O}(l) + \text{Cl}_2(g) \]
**Problem:**
How much \( \text{MnO}_2(s) \) should be added to excess \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) to obtain 105 mL of \( \text{Cl}_2(g) \) at 25 °C and 715 Torr?
**Hint:** It's another stoichiometry problem. See hints for previous problems. You will first determine \( n \), which represents moles of chlorine gas. Then, use stoichiometry to calculate moles of the reactant needed. Finally, convert this to grams of that reactant.
**Calculation:**
\[ \text{Mass:} \ \_\_\_\_\_\_\ \text{g MnO}_2 \]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff85ccebc-e9ce-4b65-8b16-ef66a279caa1%2Fd22d5529-314e-4b56-995c-ca9b348551f9%2Ffpcgjtm8_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Stoichiometry Problem: Preparing Chlorine in the Laboratory**
Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide (\( \text{MnO}_2 \)) with hydrochloric acid (\( \text{HCl(aq)} \)), as described by the chemical equation:
\[ \text{MnO}_2(s) + 4 \text{HCl(aq)} \rightarrow \text{MnCl}_2(aq) + 2 \text{H}_2\text{O}(l) + \text{Cl}_2(g) \]
**Problem:**
How much \( \text{MnO}_2(s) \) should be added to excess \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) to obtain 105 mL of \( \text{Cl}_2(g) \) at 25 °C and 715 Torr?
**Hint:** It's another stoichiometry problem. See hints for previous problems. You will first determine \( n \), which represents moles of chlorine gas. Then, use stoichiometry to calculate moles of the reactant needed. Finally, convert this to grams of that reactant.
**Calculation:**
\[ \text{Mass:} \ \_\_\_\_\_\_\ \text{g MnO}_2 \]
Expert Solution
Step 1
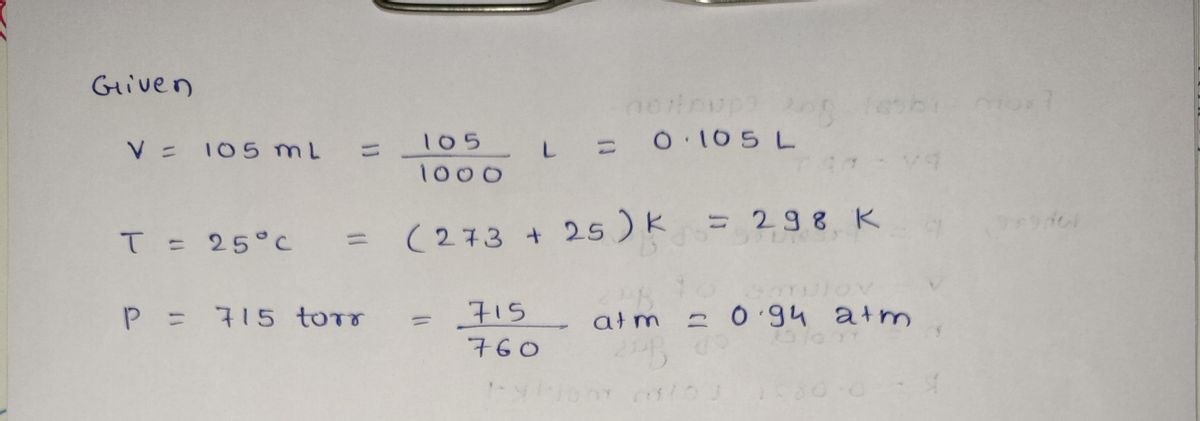
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY