
Solutions possessing any of the known weak base and a strong acid are likely to constitute buffer only when the acid's moles are lesser than the base' moles. Such solutions are recognized as "basic-buffers".
Given:
The molarity of ammonia is 0.100 M.
The volume of ammonia is 25.0 mL.
The molarity of HCl is 0.150 M.
The volume of HCl is 10.0 mL.

The reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid is shown below.
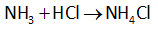
In the above reaction, 1 mole of ammonia requires 1 mole of HCl to form the salt ammonium chloride.
The formula to calculate moles is shown below.
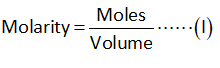
Substitute the known values of ammonia in equation (I).
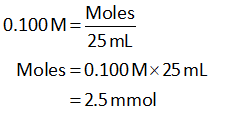
Substitute the known values of HCl in equation (I).
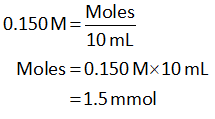
As stated above, 1 mole of ammonia completely neutralize 1 mole of HCl to form 1 mole of ammonium chloride.
Therefore, 1.5 millimoles of HCl will completely neutralize 1.5 millimoles of ammonia to give 1.5 millimoles of ammonium chloride.
Thus, the moles of ammonia left in the solution are (2.5 – 1.5) = 1.0 millimoles.
In the solution, only ammonia (weak base) and ammonium chloride (salt of weak base) are present.
Therefore, it represents a buffer.
The Henderson Hasselbalch equation for a basic buffer is shown below.
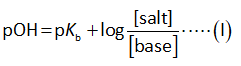
Here,
The salt is ammonium chloride.
The base is ammonia.
The pKb value is calculated as shown below.
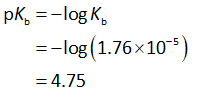
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 12 images









