A0.493 M aqueous solution of a non-electrolyte has a density of 1.063 g/mL, and a freezing point of -1.03 °C. What is the molar mass of the compound?


Colligative properties are the properties which depend on the number of atoms or molecules or ions or particles present in the solution. Some common colligative properties are depression in freezing point, elevation in boiling point, osmotic pressure and relative lowering in vapor pressure.
Depression in freezing point is a colligative property that can be calculated with the help of concentration (molality) of solution. The relation between depression in freezing point and molality of solution can be written as:'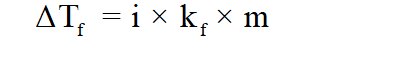
Here:
ΔTf= elevation in boiling point
kf= Molal depression constant for freezing point
i = van’t Hoff factor (depends on number of ions formed after dissociation)
m= molality (moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg)
Molarity of solution = 0.493 M
Thus moles of solute = 0.493 moles
Volume of solution = 1 L = 1000 mL
Density of solution= 1.063 g/mL
Calculate mass of solution:
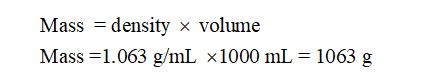
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 4 images









