
The Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory was purposed by Bronsted and Lowery is called Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give H+ ions whereas a base can accept the H+ ion in its solution. Hence this theory is entirely based on the presence of H+ ion in the given substance. It purposed the concept of conjugate acid-base pair. A Bronsted acid gives H+ ion to form conjugate base whereas a Bronsted base accepts H+ ion to form its conjugate acid.
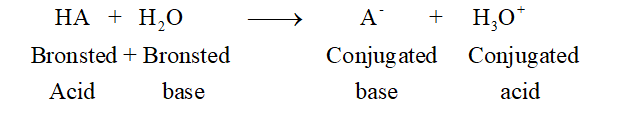
A strong acid shows complete dissociation to respective anion and H3O+whereas a weak acid can only partially ionized to its respective ions. A strong acid forms a weak conjugate base whereas a weak acid forms a strong conjugate base.
The equilibrium constant for acid dissociation is denoted as Ka. It represents the ratio of the equilibrium concentration of product and reactant molecule. Similarly the equilibrium constant for base dissociation is denoted as Kb. It represents the ratio of the equilibrium concentration of product and reactant molecule.
For conjugate-acid base pairs, the acid dissociation constant Ka and base ionization constant Kb are related by the following equations:
Ka x Kb=Kw
Here Kw Here Kw represents the auto-ionization of water.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 4 images









