Calculate eq. concentrations when for 0.55 M HAc solution where ka(25C)=1.8x10^-5 with an ICE table. Calculate the pH of solution and percent ionization. Why does this pH make sense compared to a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid?
Calculate eq. concentrations when for 0.55 M HAc solution where ka(25C)=1.8x10^-5 with an ICE table. Calculate the pH of solution and percent ionization. Why does this pH make sense compared to a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid?
Look out this reaction as:
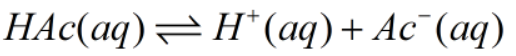
HAc: concentration of acetic acid.
H+: concentration of proton.
Ac-: concentration of acetate ion.
The Initial, Change and Equilibrium table can be drawn as-
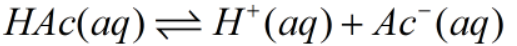
| Initial | 0.55M | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium | (0.55-x) | x | x |
Ka is the dissociation constant for the acetic acid and can be given as-
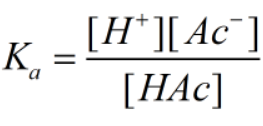
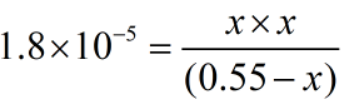
The concentration of ions are much smaller than the acid.
Therefore, x can be neglected from the denominator.
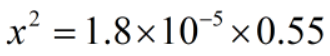
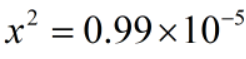
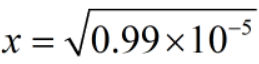
Since, x = [H+]
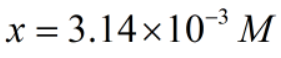
Now,
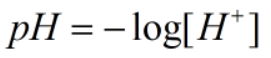
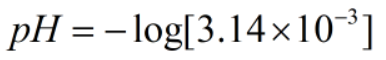
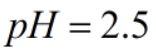
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 14 images









