(a) Determine a point estimate for the population mean. A point estimate for the population mean is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
(a) Determine a point estimate for the population mean. A point estimate for the population mean is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The image contains a table showing the t-distribution values for different degrees of freedom under various levels of significance in the right tail of the distribution. Additionally, there is a graph depicting a t-distribution curve with the shaded area representing the area in the right tail.
### Graph Explanation:
- **Title**: The graph shows a typical t-distribution curve.
- **Shaded Area**: The right tail of the curve is highlighted, indicating the area for which the values in the table are calculated.
### Table Details:
- **Columns**: The table lists t-values at specific significance levels (0.25, 0.20, 0.15, 0.10, 0.05, 0.025, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.0025, 0.001, 0.0005) for various degrees of freedom.
- **Rows**: Each row corresponds to a different degree of freedom starting from 1 up to 1000 and includes an additional row for infinity.
- **Values**: Each cell in the table represents the t-value for the specified degree of freedom and significance level.
This table is typically used in statistics to determine critical values for hypothesis testing involving t-distributions, commonly used in estimating population parameters when the sample size is small and the population standard deviation is unknown.
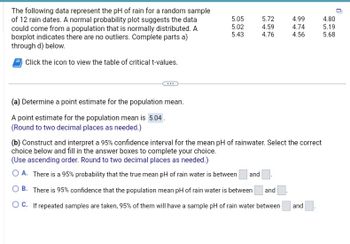
![The following data represent the pH of rain for a random sample of 12 rain dates. A normal probability plot suggests the data could come from a population that is normally distributed. A boxplot indicates there are no outliers. Complete parts a) through d) below.
| 5.05 | 5.72 | 4.99 | 4.80 |
|------|------|------|------|
| 5.02 | 4.59 | 4.74 | 5.19 |
| 5.43 | 4.76 | 4.56 | 5.68 |
**(a) Determine a point estimate for the population mean.**
A point estimate for the population mean is [input box].
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
---
**Graphical Note:** There is an option to click and view the table of critical t-values, which appears as a button labeled "Table of Critical t-Values."](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4%2F2a9954b4-f3a4-47b3-be2f-d86a2ecdc4e5%2Fy4gud65_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The following data represent the pH of rain for a random sample of 12 rain dates. A normal probability plot suggests the data could come from a population that is normally distributed. A boxplot indicates there are no outliers. Complete parts a) through d) below.
| 5.05 | 5.72 | 4.99 | 4.80 |
|------|------|------|------|
| 5.02 | 4.59 | 4.74 | 5.19 |
| 5.43 | 4.76 | 4.56 | 5.68 |
**(a) Determine a point estimate for the population mean.**
A point estimate for the population mean is [input box].
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
---
**Graphical Note:** There is an option to click and view the table of critical t-values, which appears as a button labeled "Table of Critical t-Values."
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:(c) Construct and interpret a 99% confidence interval for the mean pH of rainwater. Select the correct
choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice.
(Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.)
O A. There is a 99% probability that the true mean pH of rain water is between and
OB. If repeated samples are taken, 99% of them will have a sample pH of rain water between and
and
O C. There is 99% confidence that the population mean pH of rain water is between
Solution
Follow-up Question
Transcribed Image Text:The image provides data on the pH of rain from a random sample of 12 rain dates:
- 5.05, 5.72, 4.99, 4.80, 5.02, 4.59, 4.74, 5.19, 5.43, 4.76, 4.56, 5.68
A normal probability plot indicates the data could be from a normally distributed population, with no outliers as shown by a boxplot.
### Tasks:
#### (a) Determine a point estimate for the population mean.
- The point estimate for the population mean is calculated as **5.04** (rounded to two decimal places).
#### (b) Construct and interpret a 95% confidence interval for the mean pH of rainwater.
- Options to choose from:
- **A.** There is a 95% probability that the true mean pH of rain water is between \_\_ and \_\_.
- **B.** There is 95% confidence that the population mean pH of rain water is between \_\_ and \_\_.
- **C.** If repeated samples are taken, 95% of them will have a sample pH of rain water between \_\_ and \_\_.
- To complete this task, one would refer to a table of critical t-values and perform calculations to fill in the confidence interval values as needed, rounding to two decimal places.
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman