Briefly describe the contribution of Walter nernest,t.w Richard,max plank and g.n Lewis in the development of the third law of thermodynsmic
The third law of thermodynamic was first state by Walther Nernst during the years 1906–12 "for certain isothermal chemical reactions between solids, the entropy changes approach zero as the thermodynamic temperature approaches zero"
The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system at absolute zero is a well-defined constant. This is because a system at zero temperature exists in its ground state, so that its entropy is determined only by the degeneracy of the ground state. In 1912 Nernst stated the law thus: "It is impossible for any procedure to lead to the isotherm T = 0 in a finite number of steps.
Nernst based this statement on his analysis of experimental data obtained by T. W. Reachards, who studied the entropy changes of chemical reactions between solid as the temperature was made lower anf lower
The most common formulation of the third law of thermodynamics belongs to Max Planck who stated that Planck formulation. When temperature falls to absolute zero, the entropy of any pure crystalline substance tends to a universal constant (which can be taken to be zero)
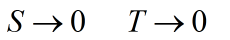
Entropy selected according to S = 0 at T = 0 is called absolute. If S depends on x (where x may represent any independent thermodynamic parameter such as volume or extent of a chemical reaction), then x is presumed to remain finite in above equation. The Planck formulation unifies other formulations given below into a single statement but has a qualifier “pure crystalline substance”, which confines application of the law to specific substances. This is not consistent with understanding the laws of thermodynamics as being the most fundamental and universally applicable principles of nature. This formulation does not comment on entropy of other substances at T = 0 and thus is not universally applicable.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









