Select the least reactive alkyl bromide in an SN1 reaction?

The unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN1) proceeds in two steps. In the first step, the leaving group removed from the substrate, and the carbocation intermediate is formed. This step is a slow and rate-determining step. The rate of this step depends on the stability of the carbocation intermediate. The higher the stability of the carbonation intermediates the higher will be the rate of reaction.
In the second step, the nucleophile adds to the carbocation intermediate to form the final product.
The increasing order of the stability of the carbonation for the even alkyl halide is as follows:
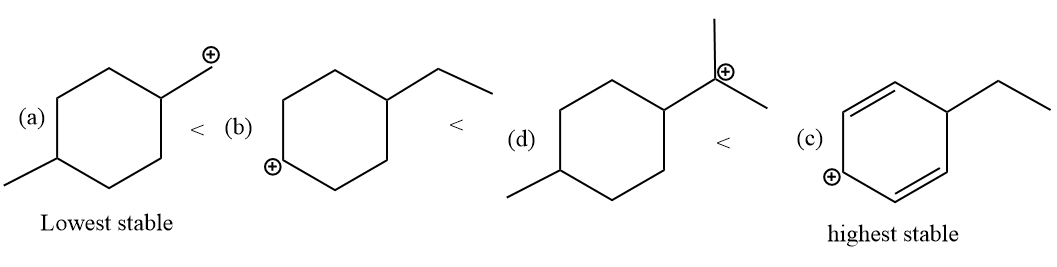
The primary carbocation is the lowest stable and the secondary allylic carbonation is the highest stable intermediate carbocation.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









