block to its acceleration a. Exercise 2 A block is pulled to the right at constant speed. 1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it moves. 2. Use Newton’s second law to relate the force F measured by the force probe to the kinetic friction force under the assumption that the block is moving with constant speed.
block to its acceleration a. Exercise 2 A block is pulled to the right at constant speed. 1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it moves. 2. Use Newton’s second law to relate the force F measured by the force probe to the kinetic friction force under the assumption that the block is moving with constant speed.
Related questions
Question
Problem 3 Friction
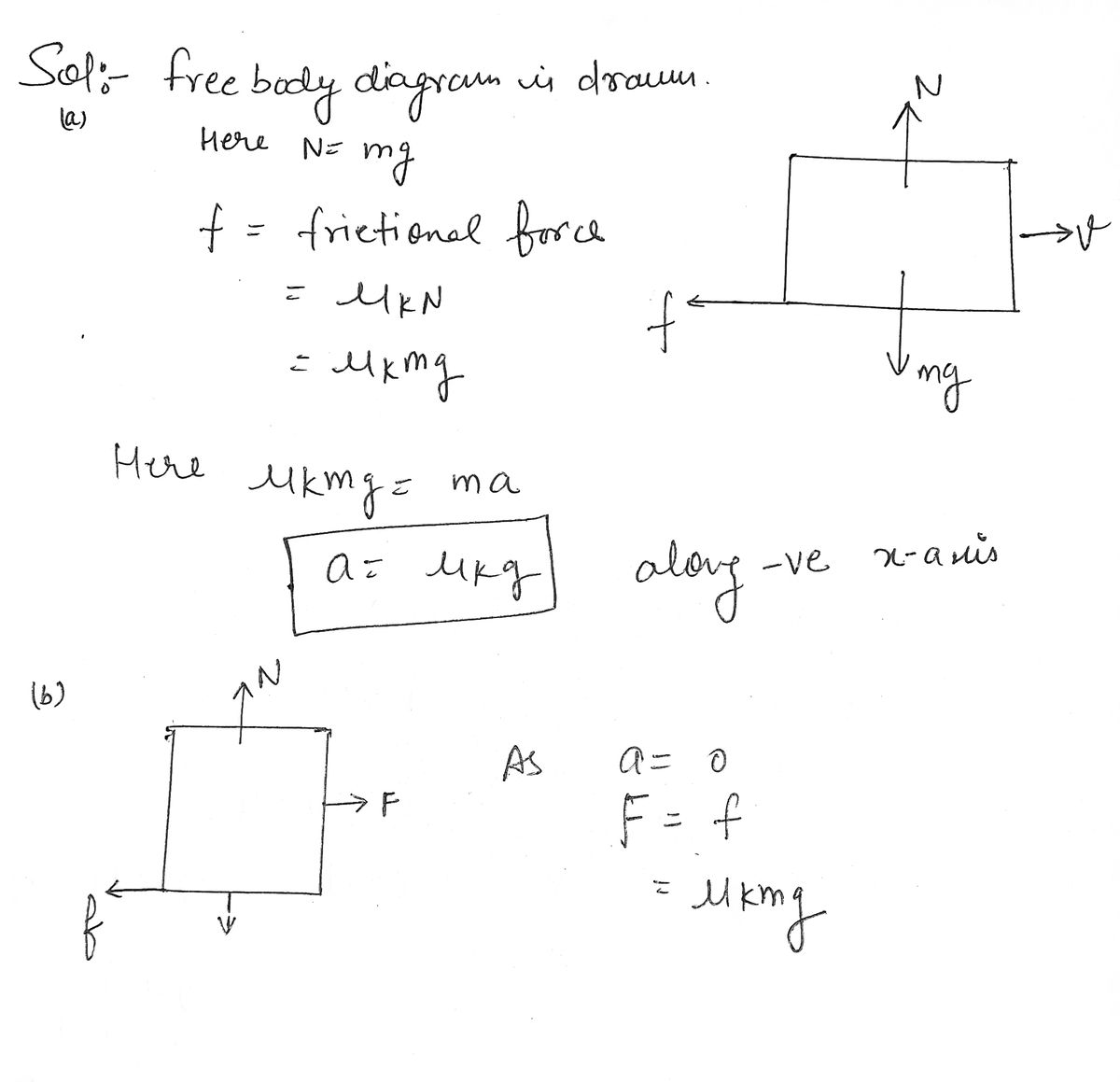
Exercise 1 A block, sliding to the right, slows down because of friction.
1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it slows.
2. Use Newton’s second law to relate the friction force that acts on the block to its acceleration a.
Exercise 2
A block is pulled to the right at constant speed.
1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it moves.
2. Use Newton’s second law to relate the force F measured by the force probe to the kinetic friction force under the assumption that the block is moving with constant speed.

Transcribed Image Text:9:30 1
Physics 1200 preLa... Q
Friction
A block, sliding to the right, slows down because of friction.
1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it slows.
+y
L.
+x
2. Use Newton's second law to relate the friction force that acts on the blocd
its acceleration a.
A block is pulled to the right at constant speed.
1. Draw a free-body diagram of the block as it moves.
+y
+x
2. Use Newton's second law to relate the force F measured by the force pr
to the kinetic friction force under the assumption that the block is mov
with constant speed.
Dashboard
Calendar
To Do
Notifications
Inbox
因
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
