Below are data from a case-control study about the risk of stroke related to the "exposure" of smoking. Cases included individuals who were hospitalized at an Atlanta hospital for stroke. Controls consisted of individuals at the same hospital for reasons not related to strokes. Smoking History Yes No Total Stroke Case 381 119 500 No Stroke Controls 610 890 1,500 Total 991 1,009 2,000 7. Estimate the odds ratio of having a stroke (or becoming a case) comparing those with and without a smoking history. Describe in words what this means.
Below are data from a case-control study about the risk of stroke related to the "exposure" of smoking. Cases included individuals who were hospitalized at an Atlanta hospital for stroke. Controls consisted of individuals at the same hospital for reasons not related to strokes. Smoking History Yes No Total Stroke Case 381 119 500 No Stroke Controls 610 890 1,500 Total 991 1,009 2,000 7. Estimate the odds ratio of having a stroke (or becoming a case) comparing those with and without a smoking history. Describe in words what this means.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

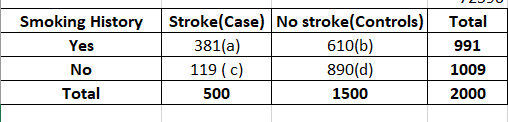
Transcribed Image Text:Below are data from a case-control study about the risk of stroke related to the "exposure" of smoking. Cases included individuals who were hospitalized at an Atlanta hospital for stroke. Controls consisted of individuals at the same hospital for reasons not related to strokes.
| Smoking History | Stroke Case | No Stroke Controls | Total |
|------------------|-------------|---------------------|-------|
| Yes | 381 | 610 | 991 |
| No | 119 | 890 | 1,009 |
| Total | 500 | 1,500 | 2,000 |
**7a.** Estimate the odds ratio of having a stroke (or becoming a case) comparing those with and without a smoking history. **Describe** in words what this means.
**7b.** If this was instead a cohort study and we were to calculate the risk ratio for this study, estimate the risk ratio (or relative risk) of having a stroke. **Describe** in words what this means.
**7c.** Is the **relative risk** of stroke for those with a smoking history (exposure +) versus those without a smoking history (exposure -) likely to be larger or smaller than the **odds ratio**? Why or why not.
**7d.** Assuming that strokes occur in less than 10% of the population, would you expect the difference between the two measures of risk (RR and OR) to be large? Why or why not. (Hint: Refer to lecture on "Measures of Disease Association")
Expert Solution
Step 1
The below data represents the case-control study about the risk of stroke related to the "exposure" of smoking.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman