Based on undrained triaxial tests of a clay with pore pressure measurement, the material is found to have a CD cohesion of 25 kPa and corresponding effective friction angle of 27°. A very slow direct shear test is then performed on a sample corresponding to the same effective stress conditions as experienced in-situ at the depth shown (16 m depth). The sample has the same orientation as the layering. Determine the total vertical and horizontal stresses corresponding to failure and the in-situ pore pressure. What is the orientation of the major principal stress with respect to the layering? (You may use the Mohr's circle). Clearly show your work and state assumptions made.
Based on undrained triaxial tests of a clay with pore pressure measurement, the material is found to have a CD cohesion of 25 kPa and corresponding effective friction angle of 27°. A very slow direct shear test is then performed on a sample corresponding to the same effective stress conditions as experienced in-situ at the depth shown (16 m depth). The sample has the same orientation as the layering. Determine the total vertical and horizontal stresses corresponding to failure and the in-situ pore pressure. What is the orientation of the major principal stress with respect to the layering? (You may use the Mohr's circle). Clearly show your work and state assumptions made.
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Concept explainers
Question

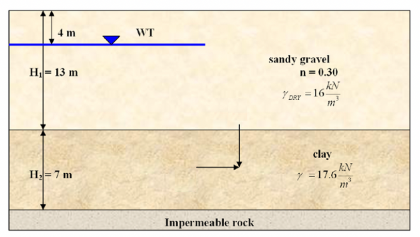
Transcribed Image Text:Based on undrained triaxial tests of a clay with pore pressure measurement, the material is found
to have a CD cohesion of 25 kPa and corresponding effective friction angle of 27°. A very slow
direct shear test is then performed on a sample corresponding to the same effective stress
conditions as experienced in-situ at the depth shown (16 m depth). The sample has the same
orientation as the layering.
Determine the total vertical and horizontal stresses corresponding to failure and the in-situ pore
pressure. What is the orientation of the major principal stress with respect to the layering? (You
may use the Mohr's circle). Clearly show your work and state assumptions made.
4 m
H₁ = 13 m
H₂= 7 m
WT
Impermeable rock
sandy gravel
n = 0.30
Y DRY
KN
3
=162
177
clay
Y = 17.6
KN
3
m³
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning