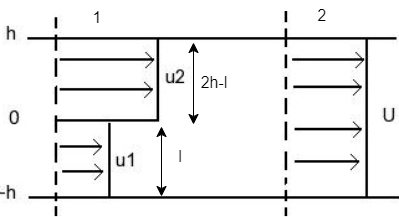
(b) I wo fluid streams with velocities u₁ and u₂ flow between parallel plates separated by a distance 2h as shown. The streams enter a mixing zone and emerge with uniform velocity U. The flow is incompressible, the pressure at each cross-section is uniform and viscous forces around the control volume are negligible. h u₁ • Find the pressure change across the mixing zone, expressed as a function of u1, U2, and corresponding mass flow rate m, m, and U. Find the lost work. When u₁ = 15 m/s, u₂ = 40 m/s, h = 25m, width = 3m, U = 25 m/s, calculate pressure change. (Hint: you cannot assume the widths of the two flow streams are h each. You will need to calculate each width)
(b) I wo fluid streams with velocities u₁ and u₂ flow between parallel plates separated by a distance 2h as shown. The streams enter a mixing zone and emerge with uniform velocity U. The flow is incompressible, the pressure at each cross-section is uniform and viscous forces around the control volume are negligible. h u₁ • Find the pressure change across the mixing zone, expressed as a function of u1, U2, and corresponding mass flow rate m, m, and U. Find the lost work. When u₁ = 15 m/s, u₂ = 40 m/s, h = 25m, width = 3m, U = 25 m/s, calculate pressure change. (Hint: you cannot assume the widths of the two flow streams are h each. You will need to calculate each width)
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
how to find the lost work? which eqn should I use? Pls help me. Thank u,

Transcribed Image Text:(b) Two fluid streams with
velocities u₁ and u2 flow between
parallel plates separated by a
distance 2h as shown. The streams
enter a mixing zone and emerge
with uniform velocity U. The flow
is incompressible, the pressure at
each cross-section is uniform and
viscous forces around the control
volume are negligible.
• Find the pressure change across the mixing zone, expressed as a function of u₁, u2,
and corresponding mass flow rate m, m₂, and U.
Find the lost work.
h
u₁
4₂
d
When u₁ = 15 m/s, u₂ = 40 m/s, h = 25m, width = 3m, U = 25 m/s, calculate pressure
change. (Hint: you cannot assume the widths of the two flow streams are h each. You
will need to calculate each width)
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
Given :
- u1 =15m/s
- u2 = 40 m/s
- h = 25 m/s
- w= 3 m
- U=25 m/s
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The