Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
100%
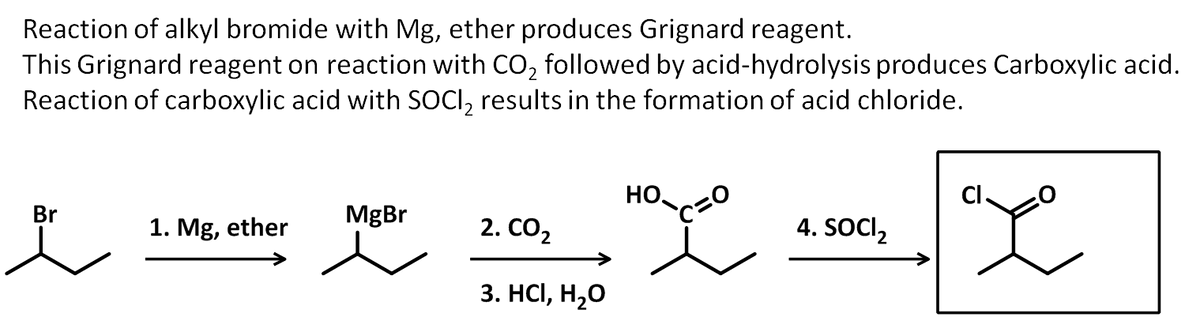
Write the products of the following sequence of reactions.

Transcribed Image Text:### Organic Chemistry Reaction Sequence
#### Starting Material:
- **2-Bromopropane**
#### Reaction Sequence:
1. **Reagent: Mg, ether**
- **Process:** Formation of a Grignard reagent. The bromine atom in 2-bromopropane reacts with magnesium in the presence of ether, forming an organomagnesium compound.
2. **Reagent: CO₂**
- **Process:** Reaction with carbon dioxide. The Grignard reagent adds to CO₂, leading to the formation of a carboxylate ion intermediate.
3. **Reagent: HCl, H₂O**
- **Process:** Hydrolysis and protonation. The carboxylate ion is treated with hydrochloric acid and water to yield a carboxylic acid.
4. **Reagent: SOCl₂**
- **Process:** Conversion to acyl chloride. The carboxylic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to form an acyl chloride.
This sequence outlines the transformation of 2-bromopropane through a series of reactions to ultimately form an acyl chloride.

Transcribed Image Text:**Diagram (b) Explanation:**
This diagram illustrates a multistep chemical reaction sequence starting with benzene. The process involves several reagents and conditions. Here is a detailed transcription and explanation of each step:
1. **Reagents: CH₃CH₂COCl, AlCl₃**
- The first step likely involves an acylation reaction using propionyl chloride (CH₃CH₂COCl) and aluminum chloride (AlCl₃) as a catalyst. This is a Friedel-Crafts acylation, which introduces an acyl group into the benzene ring.
2. **Reagents: Br₂, CH₃CO₂H**
- The second step introduces bromine (Br₂) in the presence of acetic acid (CH₃CO₂H). This suggests a bromination reaction, likely resulting in the addition of a bromine atom to the benzene ring.
3. **Reagents: K⁺ tBuO⁻**
- The third step involves potassium tert-butoxide (K⁺ tBuO⁻). This step may involve a deprotonation or elimination reaction, facilitating further transformations in the molecule.
4. **Reagents: OsO₄ then NaHSO₃**
- The fourth step uses osmium tetroxide (OsO₄) followed by sodium bisulfite (NaHSO₃). Osmium tetroxide is typically used for dihydroxylation of alkenes, suggesting this might be an oxidation step to introduce diols.
5. **Reagents: H₂CrO₄**
- The final step uses chromic acid (H₂CrO₄), commonly used for oxidations. This step may further oxidize any alcohols into carboxylic acids or ketones.
This sequence of reactions results in the transformation of benzene through various functional group interchanges and additions. Each reagent and condition is critical for the structural evolution of the initial aromatic compound.
Expert Solution
Step 1: First reaction
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY