Approximate the measures of center for following GFDT. Data Frequency 40-44 2. 45-49 50 -54 15 55-59 22 60 64 14 Report mode and median accurate to one decimal place. Report the mean accurate to two decimal places (or enter as a fraction). (a) mode = (b) median = (C) mean =
Inverse Normal Distribution
The method used for finding the corresponding z-critical value in a normal distribution using the known probability is said to be an inverse normal distribution. The inverse normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with a family of two parameters.
Mean, Median, Mode
It is a descriptive summary of a data set. It can be defined by using some of the measures. The central tendencies do not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset. However, they give a summary of the data set. The central tendency or measure of central tendency is a central or typical value for a probability distribution.
Z-Scores
A z-score is a unit of measurement used in statistics to describe the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean, measured with reference to standard deviation from the mean. Z-scores are useful in statistics because they allow comparison between two scores that belong to different normal distributions.

Mean: The mean is the sum of observations divided by the number of observations. that is,
Mean =
Notations:
The sample mean = and
Population mean = μ
Median: The median is the value of the middlemost observation in the data set when the observation is arranged in increasing (or decreasing) order of their values.
The formula for median:
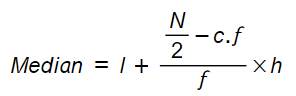
Were,
l: is the lower-class boundary of the quartile class.
N: is the total frequency of the distribution
c.f: is the cumulative frequency before the quartile class.
f: is the frequency of the quartile class.
h: is the class size
Mode: The mode is the value that is repeated maximum times.
we can denote it by Mo.
The formula for mode is,
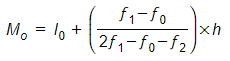
Were,
l0 = lower limit of the model class.
h = size of the class interval (assuming all class sizes to be equal).
f1 = frequency of the model class.
f0 = frequency of the class preceding the model class.
f2 = frequency of the class succeeding the model class.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images









