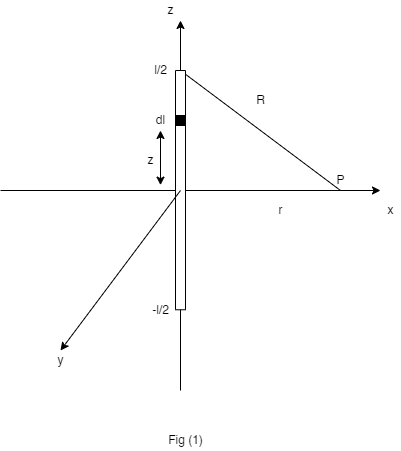
V for a linear charge of length I and charge density Pl at a point b in the x-y plane from the origin Find its electrical potential. The line coincides with the charge z-axis and extends from z=-l/2 to z=1/2.
V for a linear charge of length I and charge density Pl at a point b in the x-y plane from the origin Find its electrical potential. The line coincides with the charge z-axis and extends from z=-l/2 to z=1/2.
Related questions
Question
V for a linear charge of length l and charge density Pl at a point b in the x-y plane from the origin Find its electrical potential. The line coincides with the charge z-axis and extends from z=-l/2 to z=1/2.

Transcribed Image Text:V for a linear charge of length I and charge density Pl at a point b in
the x-y plane from the origin
Find its electrical potential. The line coincides with the charge z-axis
and extends from z=-l/2 to z=1/2.
Expert Solution
Concept and Principle:
The voltage or electric potential is defined as the work done to move a particle from one point to another in an electric field. In the given system we have a linear charge which supplies the electric field. Voltage can be written as,
Here Q is the charge, r is the distance to the point from the charge, and ε0 is the vacuum permittivity.
The given system can be drawn as,
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images
