A uniformly charged rod of length L and total charge Q lies along the x axis as shown in in the figure below. (Use the following as necessary: Q, L, d, and k..) d L (a) Find the components of the electric field at the point P on the y axis a distance d from the origin. E = Ey = (b) What are the approximate values of the field components when d >> L? Ey= Explain why you would expect these results.
A uniformly charged rod of length L and total charge Q lies along the x axis as shown in in the figure below. (Use the following as necessary: Q, L, d, and k..) d L (a) Find the components of the electric field at the point P on the y axis a distance d from the origin. E = Ey = (b) What are the approximate values of the field components when d >> L? Ey= Explain why you would expect these results.
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:A uniformly charged rod of length L and total charge Q lies along the x axis as shown in in the figure below. (Use the following as necessary: Q, L, d, and k.)
P
d
L
(a) Find the components of the electric field at the point P on the y axis a distance d from the origin.
Ex
=
Ey =
(b) What are the approximate values of the field components when d >> L?
Ey
Explain why you would expect these results.
Expert Solution
Step 1
According to Coulomb's law the electric field at a point (x,y) due to a charge q at (x',y') is given by,
Consider the situation as below,
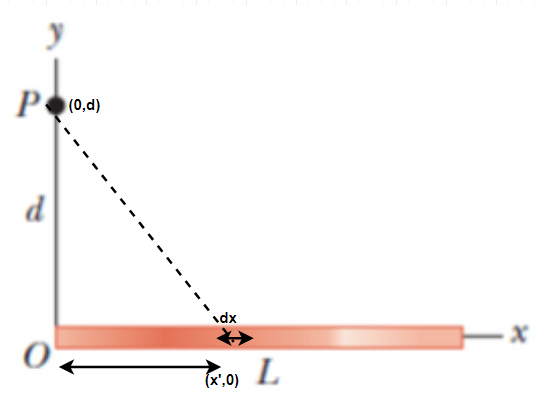
Let the linear charge density of the charge on the rod be,
Then the electric field at (x,y)=(0,d) due to a differential length element dx of the charged rod positioned at (x',y')=(x',0) having charge , using (1) is,
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images
