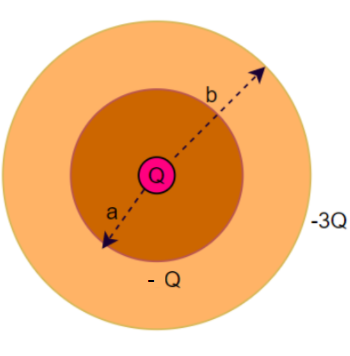
a This is a conducting outer shell of inner radius a and outer radius b. There's a point charge Q in the middle. The shell itself has total charge -3Q. Use spherical gaussian surfaces to find the electric field for rb. What is the surface charge density on the inside of the shell and on the outside of the shell? Draw the E-field lines. -3Q
a This is a conducting outer shell of inner radius a and outer radius b. There's a point charge Q in the middle. The shell itself has total charge -3Q. Use spherical gaussian surfaces to find the electric field for rb. What is the surface charge density on the inside of the shell and on the outside of the shell? Draw the E-field lines. -3Q
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:a
This is a conducting outer shell of inner radius a and outer
radius b. There's a point charge Q in the middle. The shell
itself has total charge -3Q. Use spherical gaussian surfaces
to find the electric field for r<a, a<r<b, and r>b. What is the
surface charge density on the inside of the shell and on the
outside of the shell? Draw the E-field lines.
-30
Expert Solution
Step 1
According to Gauss' law the electric flux out of a volume is proportional to charge contained inside the volume, mathematically speaking,
Where the closed surface integral is done over the surface containing the volume.
In the given problem a charge Q is present at the center of a conducting shell with radius and itself having total charge -3Q,
The Q at center induces an equal and opposite charge at the inner surface of the conducting sphere.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images
