a) The potential on the outer surface of the membrane is +65.4 mV greater than that on the inside surface. How much charge resides on the outer surface? (b) If the charge in part (a) is due to K+ ions (charge +e), how many such ions are present on the outer surface?
The membrane that surrounds a certain type of living cell has a surface area of 5.45 10-9 m2 and a thickness of 9.90 10-9 m. Assume that the membrane behaves like a parallel plate capacitor and has a dielectric constant of 5.50.
(b) If the charge in part (a) is due to K+ ions (charge +e), how many such ions are present on the outer surface?
A capacitor is a system of two conductors carrying equal and opposite charges placed at a very short distance. For a capacitor, the charge on a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between the conductor.
is a constant and is known as the capacitance. The SI unit of capacitance is Farad . One of the most common capacitors is a parallel plate capacitor where two plates of equal dimension and carrying opposite charge density are placed at a very short distance.
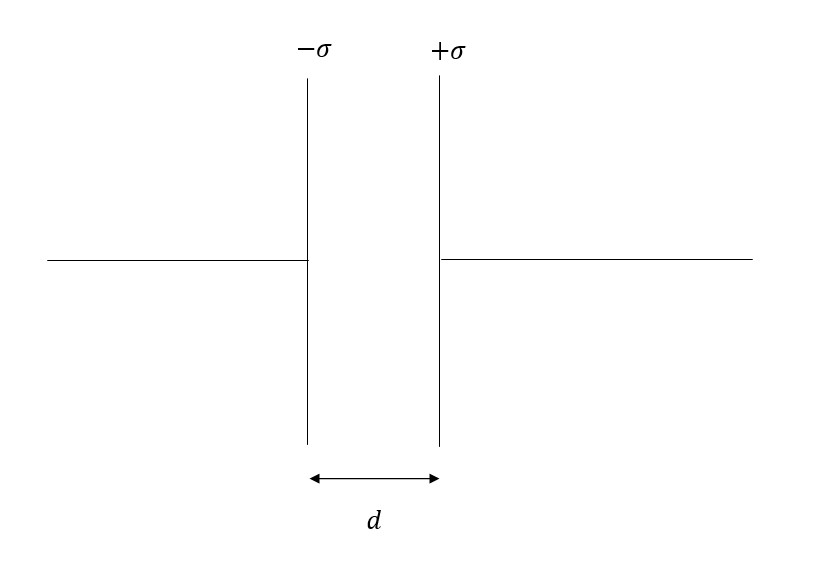
Let the distance between the plates be and the surface area of the plates be . The electric field between the plates
is the dielectric constant of the material between the plates. We know that the charge on the plates
This gives
The potential difference between the plates
Therefore the capacitance of the capacitor
In the given question we have the surface area of the cell
the thickness of the cell
The dielectric constant of the medium
Therefore the capacitance of the cell wall
a. The potential difference between the walls
Therefore the charge that resides on the surface is
b. Potassium ions carry unit of charge. Let the number of potassium ions be N. Therefore by quantization of charge we have
This gives
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images
