A straight and piecewise uniform bar ABCD of total length L is in Case 1 fixed at A in case 1 and in Case 2 fixed at both ends A and D. AB = BC = CD = L/3. The cross section area of segment CD is half of the area of the segment ABC, i.e. AABC = ACB. A point load of P is applied at B. Assume that bar material is linear and elastic and the modulus of elasticity is E
A straight and piecewise uniform bar ABCD of total length L is in Case 1 fixed at A in case 1 and in Case 2 fixed at both ends A and D. AB = BC = CD = L/3. The cross section area of segment CD is half of the area of the segment ABC, i.e. AABC = ACB. A point load of P is applied at B. Assume that bar material is linear and elastic and the modulus of elasticity is E
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
A straight and piecewise uniform bar ABCD of total length L is in Case 1 fixed at A in case 1 and in Case 2 fixed at both ends A and D. AB = BC = CD = L/3. The cross section area of segment CD is half of the area of the segment ABC, i.e. AABC = ACB. A point load of P is applied at B. Assume that bar material is linear and elastic and the modulus of elasticity is E.

Transcribed Image Text:В
C
D
В
C
P
-L
L
-L
3
Figure 1: Case 1: bar is fixed at A
Figure 2: Case 2: bar is fixed at A and D
L = 90cm, E = 70GPA, AcD= 4 cm? , P = 10KN
For both Cases:
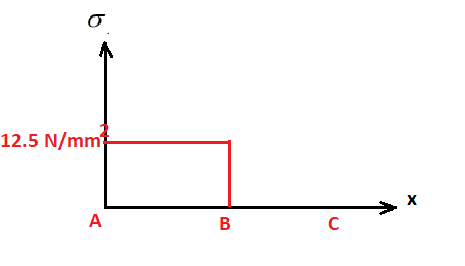
a) Find the average normal stress on a perpendicular cross-section along the bar in terms
of the plot:
Average normal stress
x Position of the
A
В
cross section
b) Find the new length of segment ABC after deformation
(Note: Case 2 is a statically indeterminate case)
1/3
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY