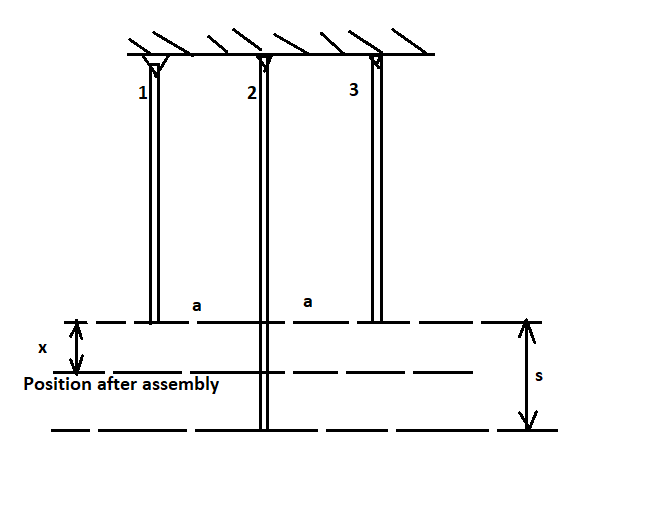
A rigid block (neglect its weight) is to be supported by three equally spaced rods (spaced by a distance a), each of which has Young's modulus E, cross section area A and length L. The rods are to be pinned to the block, but during assembly it is found that one of the bars is slightly too long; before it is attached its pin-hole extends a small distance s beneath the corresponding hole in the block. To finish the assembly, the ʻover-sized bar' is compressed and attached to the block, and then the assembly is released. (1) Find the force that is induced in each of the three bars in terms of parameters E, A, L, s and a (note that you may not need all of them). (2) After the assembly, we increase the temperature of the first and the third rod (temperature of the second rod is kept the same). The thermal expansion coefficient is a. Is it possible to achieve zero forces in the first and third rod (F1 = F3 = 0) during the heating process? If yes, find the required temperature increase AT, in terms of E, A, L, s, a and a (note that you may not need all of them). If no, explain the reason.
A rigid block (neglect its weight) is to be supported by three equally spaced rods (spaced by a distance a), each of which has Young's modulus E, cross section area A and length L. The rods are to be pinned to the block, but during assembly it is found that one of the bars is slightly too long; before it is attached its pin-hole extends a small distance s beneath the corresponding hole in the block. To finish the assembly, the ʻover-sized bar' is compressed and attached to the block, and then the assembly is released. (1) Find the force that is induced in each of the three bars in terms of parameters E, A, L, s and a (note that you may not need all of them). (2) After the assembly, we increase the temperature of the first and the third rod (temperature of the second rod is kept the same). The thermal expansion coefficient is a. Is it possible to achieve zero forces in the first and third rod (F1 = F3 = 0) during the heating process? If yes, find the required temperature increase AT, in terms of E, A, L, s, a and a (note that you may not need all of them). If no, explain the reason.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Please show all work thanks

Transcribed Image Text:A rigid block (neglect its weight) is to be supported by three equally spaced rods (spaced by a
distance a), each of which has Young's modulus E, cross section area A and length L. The rods
are to be pinned to the block, but during assembly it is found that one of the bars is slightly too
long; before it is attached its pin-hole extends a small distance s beneath the corresponding hole in
the block. To finish the assembly, the 'over-sized bar' is compressed and attached to the block,
and then the assembly is released.
(1) Find the force that is induced in each of the three bars in terms of parameters E, A, L, s
and a (note that you may not need all of them).
(2) After the assembly, we increase the temperature of the first and the third rod (temperature of
the second rod is kept the same). The thermal expansion coefficient is a. Is it possible to achieve
zero forces in the first and third rod (F, = F3 = 0) during the heating process? If yes, find the
required temperature increase AT, in terms of E, A, L, s, a and a (note that you may not need all
of them). If no, explain the reason.
Note: please draw clear free body diagrams.
%3D
2
2
B"
Eata
Expert Solution
Step 1
The schematic diagram is
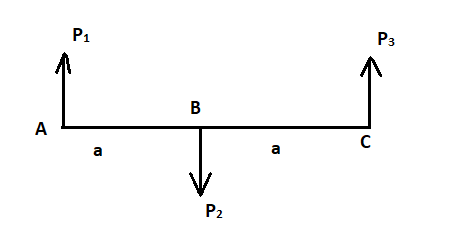
Free body diagram of the rigid block
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY