A rare form of malignant tumor occurs in 11 children in a million, so its probability is 0.000011. Four cases of this tumor occurred in a certain town, which had 14,318 children. Assuming that this tumor occurs as usual, find the mean number of cases in groups of 14,318 children. Using the unrounded mean from part (a), find the probability that the number of tumor cases in a group of 14,318 children is 0 or 1. What is the probability of more than one case? Does the cluster of four cases appear to be attributable to random chance? Why or why not? (*Need before midnight pleeeease!)
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
A rare form of malignant tumor occurs in 11 children in a million, so its probability is 0.000011. Four cases of this tumor occurred in a certain town, which had 14,318 children.
- Assuming that this tumor occurs as usual, find the mean number of cases in groups of 14,318 children.
- Using the unrounded mean from part (a), find the probability that the number of tumor cases in a group of 14,318 children is 0 or 1.
- What is the probability of more than one case?
- Does the cluster of four cases appear to be attributable to random chance? Why or why not?
(*Need before midnight pleeeease!)
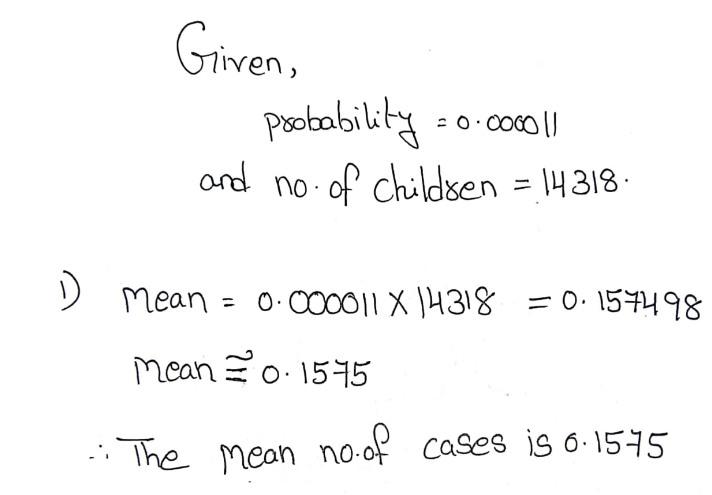
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









