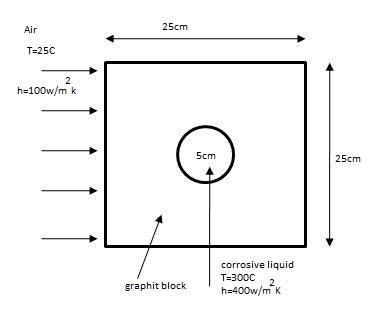
A highly corrosive liquid is cooled by passing it through a circular channel with a diameter of 5 cm drilled in a rectangular block of graphite (k = 800 W/mK). Ambient air is blown over the exterior of the block as shown in the sketch below. The heat-transfer coefficient for the air is 100 W/m² K, based on the total exterior surface area of the block. Calculate the rate of heat loss from the liquid per meter of channel length.
A highly corrosive liquid is cooled by passing it through a circular channel with a diameter of 5 cm drilled in a rectangular block of graphite (k = 800 W/mK). Ambient air is blown over the exterior of the block as shown in the sketch below. The heat-transfer coefficient for the air is 100 W/m² K, based on the total exterior surface area of the block. Calculate the rate of heat loss from the liquid per meter of channel length.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
i dont know how to equate the 3 equations to each other to solve for heat loss
answer is given.
![(2.12) A highly corrosive liquid is cooled by passing it through a circular channel with a diameter of 5 cm drilled in a rectangular
block of graphite (k = 800 W/mK). Ambient air is blown over the exterior of the block as shown in the sketch below. The
heat-transfer coefficient for the air is 100 W/m² K, based on the total exterior surface area of the block. Calculate the rate of
heat loss from the liquid per meter of channel length.
Ans. 10,500 W/m of length.
Ssquare=
2πL
In (1.08w)
q=kSAT
Air
T = 25°C
h = 100 W/m².K
Conduction
S = 3.726m & q = 2980.8(Ts T₂) [¹]
Convection from Liq→ Surface
q = 125.66(573K - Ts) [2]
Convection Blocksurface → air
q = h∞AAT
q = 100(T₂-298) [3]
Steady state all should (=)
Graphite
block
25 cm
25 cm
Corrosive liquid
T = 300°C
h = 400 W/m².K](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff4dfc165-1571-419f-99fc-a4587d76c340%2F0710b4a1-e40c-415d-9368-e38bd836c7b8%2F5ppir5y_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:(2.12) A highly corrosive liquid is cooled by passing it through a circular channel with a diameter of 5 cm drilled in a rectangular
block of graphite (k = 800 W/mK). Ambient air is blown over the exterior of the block as shown in the sketch below. The
heat-transfer coefficient for the air is 100 W/m² K, based on the total exterior surface area of the block. Calculate the rate of
heat loss from the liquid per meter of channel length.
Ans. 10,500 W/m of length.
Ssquare=
2πL
In (1.08w)
q=kSAT
Air
T = 25°C
h = 100 W/m².K
Conduction
S = 3.726m & q = 2980.8(Ts T₂) [¹]
Convection from Liq→ Surface
q = 125.66(573K - Ts) [2]
Convection Blocksurface → air
q = h∞AAT
q = 100(T₂-298) [3]
Steady state all should (=)
Graphite
block
25 cm
25 cm
Corrosive liquid
T = 300°C
h = 400 W/m².K
Expert Solution
Step 1
To Find :
The rate of heat loss from the liquid.
Given :
The diameter of hole is
The thermal conductivity of graphite block is
The heat transfer coefficient for the air is
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY