A buffer can be prepared from a weak acid, HA, and it's conjugate base, A. A 1L solution is prepared in which the concentrations are [HA] = 0.2M and [A¯] = 0.1 M. The pka of HA is 7.5. What is the pH of this solution before and after 50 ml of 1M KOH, a strong base, is added? A) before pH = 7.2, after pH = 7.5 %3D B) before pH = 7.7, after pH = 8.0 %3D C) before pH = 7.0, after pH = 6.6 %3D %3D D) before pH = 7.0, after pH = 7.4 %3D
![A buffer can be prepared from a weak acid, HA, and it's conjugate base, A. A 1L
solution is prepared in which the concentrations are [HAJ] = 0.2M and [A] = 0.1 M.
The pKa of HA is 7.5. What is the pH of this solution before and after 50 ml of 1M
%3D
KOH, a strong base, is added?
A) before pH = 7.2, after pH = 7.5
B) before pH = 7.7, after pH = 8.0
%3D
%3D
C) before pH = 7.0, after pH = 6.6
%3D
%D
D) before pH = 7.0, after pH = 7.4
%3D](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbe7fb550-605d-4f07-b463-aa224e287929%2F3c2b4c7d-64e4-4207-8470-38f70150a947%2Fcgwjuls_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Given : Volume of buffer solution = 1 L
[HA] i.e concentration of weak acid HA = 0.2 M
[A- ] i.e the concentration of conjugate base of weak acid HA = 0.1 M
Volume of KOH solution added = 50 mL = 0.050 L (since 1 L = 1000 mL)
And concentration of KOH added = 1 M
Since moles = concentration X volume of solution in L
=> Moles of HA = 0.2 X 1 = 0.2 mol.
Moles of A- = 0.1 X 1 = 0.1 mol.
And moles of KOH added = 1 X 0.050 = 0.050 mol.
Initially the solution is having weak acid and its conjugate base. Hence the initial solution is an acid buffer solution.
Since the pH of monoprotic acid buffer is given by Henderson-Hasselbalch equation as
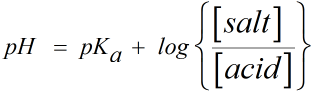
where pKa = -log(Ka ) = 7.5
[salt] = concentration of conjugate base of acid i.e A- = 0.1 M
[acid] = concentration of acid i.e HA = 0.2 M
Hence substituting the values we get,
Hence the pH before the addition of KOH = 7.2
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









