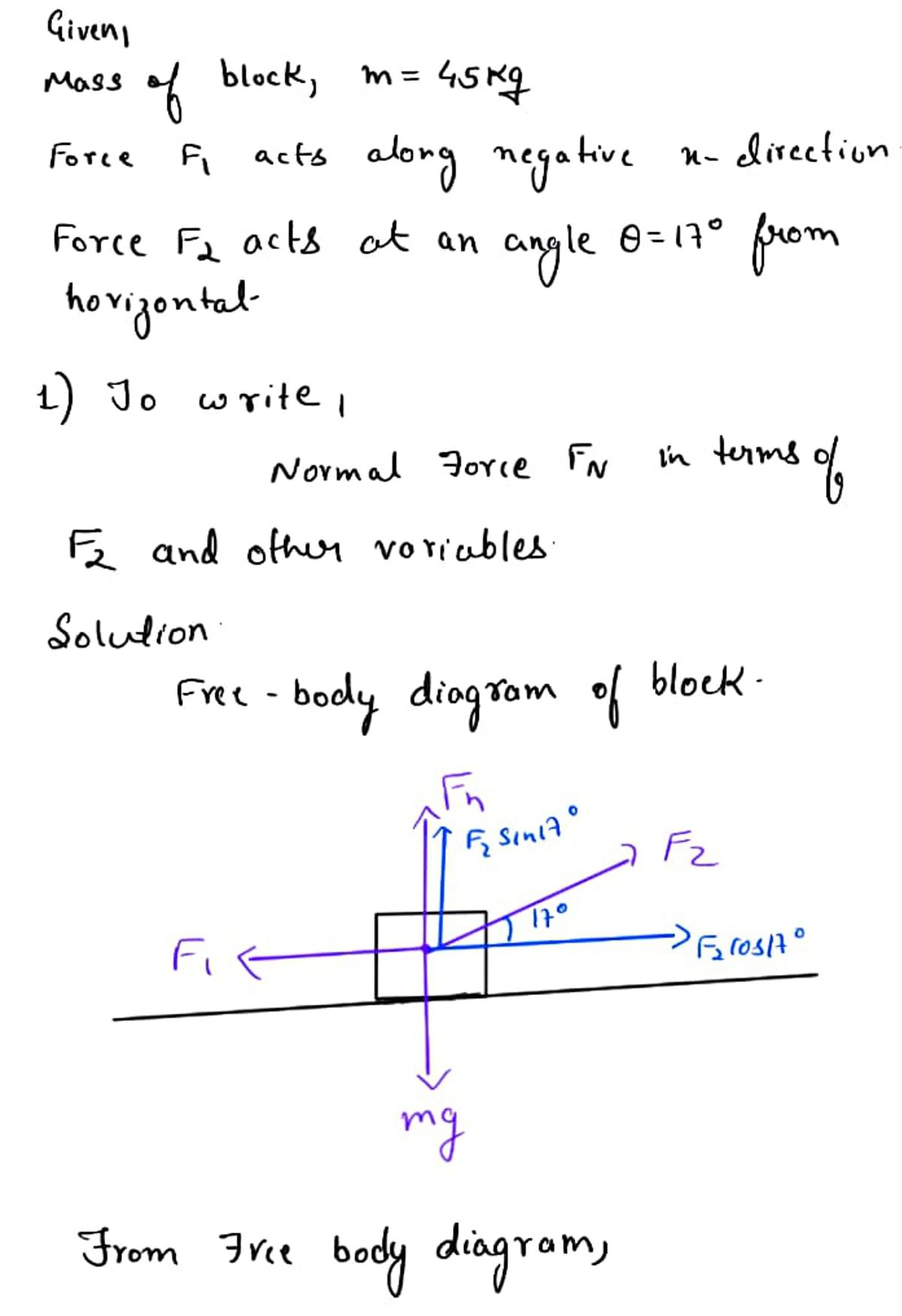
A block with a mass of m = 45 kg rests on a frictionless surface and is subject to two forces acting on it. The first force is directed in the negative x-direction with a magnitude of F1. The second has a magnitude of F2 and acts on the body at an angle θ = 17° measured from horizontal, as shown. 1) Write an expression for the magnitude of the normal force, FN, acting on the block, in terms of F2 and the other variables of the problem. Assume that the surface it rests on is rigid. 2) The two forces change such that F1 = 9.5 N and F2 = 23.5 N. Based on this change, the block may no longer be in static equilibrium. Find the block's acceleration in the x-direction, ax, in meters per second squared.
A block with a mass of m = 45 kg rests on a frictionless surface and is subject to two forces acting on it. The first force is directed in the negative x-direction with a magnitude of F1. The second has a magnitude of F2 and acts on the body at an angle θ = 17° measured from horizontal, as shown.
1) Write an expression for the magnitude of the normal force, FN, acting on the block, in terms of F2 and the other variables of the problem. Assume that the surface it rests on is rigid.
2) The two forces change such that F1 = 9.5 N and F2 = 23.5 N. Based on this change, the block may no longer be in static equilibrium. Find the block's acceleration in the x-direction, ax, in meters per second squared.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









