A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge of the roof on its way down, as shown in the figure below. (a) Find the time needed for the ball to return to the height from which it was thrown and the velocity of the ball at that instant. Analysis: 1. To find the time from a to c, we can apply v= vo+ at. What are the initial and final velocities? Hint: a→b and b→c are symmetrical. 2. Can we use another way to find the time from a to c? Hint: if we can find the time from a to b, then.. 1 = 2.04 s Imax = 20.4 m v = 0 a. t= 0 Yo = 0 = 20.0 m 1 = 4.08 s y = 0 v = -20.0 m/s 1= 5.00 s y = -22.5 m v = -29.0 m/s 50.0 m (b) Find the time needed for the ball to reach the ground and the velocity of the ball at that instant. Analysis: 1. Since we already know the time from a to c, if we can find the time from c to d, we can then find the total time needed for the ball to reach the ground. 2. To find the velocity at point d, we can apply v² = v3 + 2a(x – xo) for the process of c→d. What is the value of the displacement x – x, here? What is the value of the acceleration here? 3. We can then apply v = vo+ at to find the time from a to c. - 1 = 5.83 s y = -50.0 m v = -37.1 m/s
A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge of the roof on its way down, as shown in the figure below. (a) Find the time needed for the ball to return to the height from which it was thrown and the velocity of the ball at that instant. Analysis: 1. To find the time from a to c, we can apply v= vo+ at. What are the initial and final velocities? Hint: a→b and b→c are symmetrical. 2. Can we use another way to find the time from a to c? Hint: if we can find the time from a to b, then.. 1 = 2.04 s Imax = 20.4 m v = 0 a. t= 0 Yo = 0 = 20.0 m 1 = 4.08 s y = 0 v = -20.0 m/s 1= 5.00 s y = -22.5 m v = -29.0 m/s 50.0 m (b) Find the time needed for the ball to reach the ground and the velocity of the ball at that instant. Analysis: 1. Since we already know the time from a to c, if we can find the time from c to d, we can then find the total time needed for the ball to reach the ground. 2. To find the velocity at point d, we can apply v² = v3 + 2a(x – xo) for the process of c→d. What is the value of the displacement x – x, here? What is the value of the acceleration here? 3. We can then apply v = vo+ at to find the time from a to c. - 1 = 5.83 s y = -50.0 m v = -37.1 m/s
Related questions
Question
100%
Please help with 1b

Transcribed Image Text:A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial
height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge of the roof on its way down, as shown in the
figure below.
(a) Find the time needed for the ball to return to the height from which it was thrown
and the velocity of the ball at that instant.
Analysis:
1. To find the time from a to c, we can apply v = vo + at. What are the initial and
final velocities? Hint: a→b and b→c are symmetrical.
2. Can we use another way to find the time from a to c? Hint: if we can find the
time from a to b, then...
t = 2.04 s
I'max = 20.4 m
v = (0
a
t = 0
Yo = 0
vo = 20.0 ms
t = 4.08 s
y = 0
v = -20.0 m/s
t = 5.00 s
y = -22.5 m
v = -29.0 m/s
50.0 m
(b) Find the time needed for the ball to reach the ground and the velocity of the ball at
that instant.
Analysis:
1. Since we already know the time from a to c, if we can find the time from c to d,
we can then find the total time needed for the ball to reach the ground.
2. To find the velocity at point d, we can apply v² = vở + 2a(x – xo) for the
process of c-d. What is the value of the displacement x – x, here? What is
the value of the acceleration here?
3. We can then apply v = Vo + at to find the time from a to c.
t = 5.83 s
y = -50.0 m
v = -37.1 m/s
Expert Solution
Step 1
(b)
Take the upward direction positive as per convention.
The time (t’) from c to d may be determined from the ball’s displacement (y) from c to d, the speed (u) at c, and the gravitational acceleration (g) in the second kinematical equation as follows:
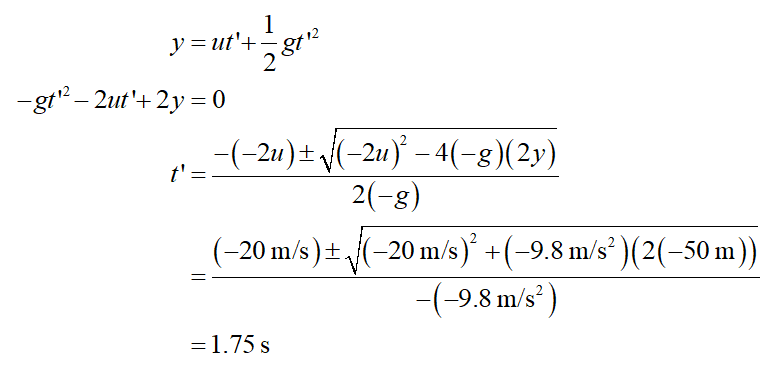
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
