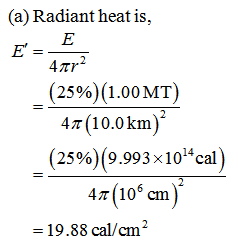
A 1.00-MT bomb exploded a few kilometers above theground deposits 25.0% of its energy into radiant heat.(a) Find the calories per cm2 at a distance of 10.0 km byassuming a uniform distribution over a spherical surface ofthat radius.(b) If this heat falls on a person’s body, what temperatureincrease does it cause in the affected tissue, assuming it isabsorbed in a layer 1.00-cm deep?
Radioactive decay
The emission of energy to produce ionizing radiation is known as radioactive decay. Alpha, beta particles, and gamma rays are examples of ionizing radiation that could be released. Radioactive decay happens in radionuclides, which are imbalanced atoms. This periodic table's elements come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Several of these kinds are stable like nitrogen-14, hydrogen-2, and potassium-40, whereas others are not like uranium-238. In nature, one of the most stable phases of an element is usually the most prevalent. Every element, meanwhile, has an unstable state. Unstable variants are radioactive and release ionizing radiation. Certain elements, including uranium, have no stable forms and are constantly radioactive. Radionuclides are elements that release ionizing radiation.
Artificial Radioactivity
The radioactivity can be simply referred to as particle emission from nuclei due to the nuclear instability. There are different types of radiation such as alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Along with these there are different types of decay as well.
A 1.00-MT bomb exploded a few kilometers above the
ground deposits 25.0% of its energy into radiant heat.
(a) Find the calories per cm2 at a distance of 10.0 km by
assuming a uniform distribution over a spherical surface of
that radius.
(b) If this heat falls on a person’s body, what temperature
increase does it cause in the affected tissue, assuming it is
absorbed in a layer 1.00-cm deep?
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









