94 Figure 35-57 shows an opti- cal fiber in which a central plastic core of index of refraction n, = 1.58 is surrounded by a plastic sheath of index of refraction n, = 1.53. Light can travel along dif- ferent paths within the central core, leading to different travel times through the fiber. This causes an initially short pulse of light to spread as it travels along the fiber, resulting in information loss. Consider light that travels directly along the central axis of the fiber and light that is repeatedly reflected at the critical angle along the core-sheath interface, reflecting from side to side as it travels down the central core. If the fiber length is 300 m, what is the difference in the travel times along these two routes? Figure 35-57 Problem 94.
94 Figure 35-57 shows an opti- cal fiber in which a central plastic core of index of refraction n, = 1.58 is surrounded by a plastic sheath of index of refraction n, = 1.53. Light can travel along dif- ferent paths within the central core, leading to different travel times through the fiber. This causes an initially short pulse of light to spread as it travels along the fiber, resulting in information loss. Consider light that travels directly along the central axis of the fiber and light that is repeatedly reflected at the critical angle along the core-sheath interface, reflecting from side to side as it travels down the central core. If the fiber length is 300 m, what is the difference in the travel times along these two routes? Figure 35-57 Problem 94.
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:94 Figure 35-57 shows an opti-
cal fiber in which a central plastic
core of index of refraction n, =
1.58 is surrounded by a plastic
sheath of index of refraction n, =
1.53. Light can travel along dif-
ferent paths within the central
core, leading to different travel times through the fiber. This causes an
initially short pulse of light to spread as it travels along the fiber,
resulting in information loss. Consider light that travels directly along
the central axis of the fiber and light that is repeatedly reflected at the
critical angle along the core-sheath interface, reflecting from side to
side as it travels down the central core. If the fiber length is 300 m,
what is the difference in the travel times along these two routes?
Figure 35-57 Problem 94.
Expert Solution
Step 1
The value of critical angle is,
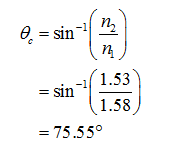
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON