A fluid can be cooled by allowing for an expansion in an insulated cylinder against a constant pressure. For an ideal gas in Houston , TX, what is the lowest possible temperature that can be reached in such a process? We will assume a monatomic gas, and no friction.

The Joule–Thomson effect describes the temperature change of a gases when it is forced through a valve or porous plug while keeping it insulated so that no heat is exchanged with the environment.
The Joule thompson coefficient of a gas is given by the formula
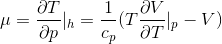
Now,
For an ideal gas,
pV = nRT
SO,
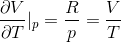
Hence, we get
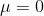
The Joult thompson coefifcient of an ideal gas is zero.
It means that an ideal gas can not change temperature for such an expansion, and It is only possible for real gases.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images









