6. An object is positioned near a convex spherical mirror as below. (Numbers are provided to help you count grid lines.) (a) Draw a ray trace using any two principal rays. (b) Confirm the position of the image and the magnification mathematically.
6. An object is positioned near a convex spherical mirror as below. (Numbers are provided to help you count grid lines.) (a) Draw a ray trace using any two principal rays. (b) Confirm the position of the image and the magnification mathematically.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Exercise 6**
An object is positioned near a convex spherical mirror as depicted below. (Numbers are provided to help you count grid lines.)
(a) Draw a ray trace using any two principal rays.
(b) Confirm the position of the image and the magnification mathematically.
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a horizontal grid with a convex mirror. The object is positioned on the left side of the mirror along the principal axis, marked at the grid line corresponding to the number 10 to the left of the mirror. The mirror is labeled as 'convex mirror' and is located to the right, with its surface curving outward. The center of curvature, marked as 'R', is labeled at point 10 to the right of the mirror. Grid lines are numbered in intervals of 5 on either side of the mirror.
The task requires drawing a ray trace using two principal rays and mathematically confirming the image position and magnification.
Expert Solution
Step 1
(a)
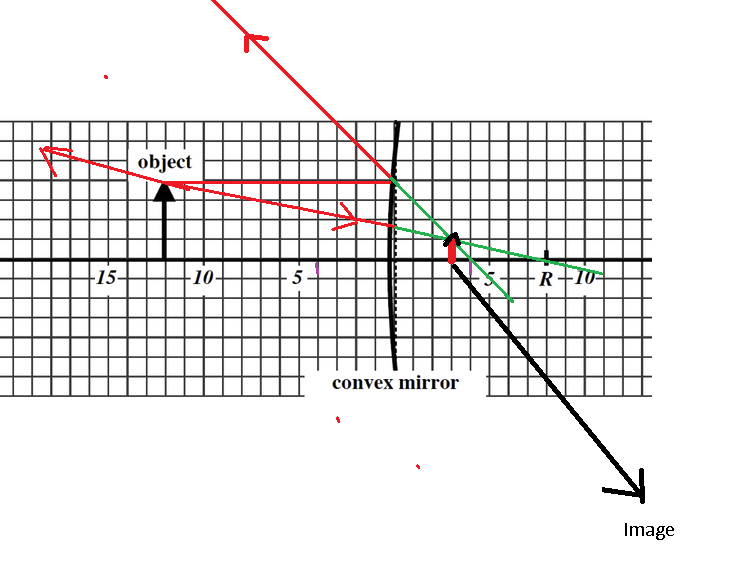
Image is formed behind the mirror.
F represents the focus of the mirror.
Position of the image is 3 units right of the mirror.
Magnification of the image is ratio of height of image to the height of object.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
