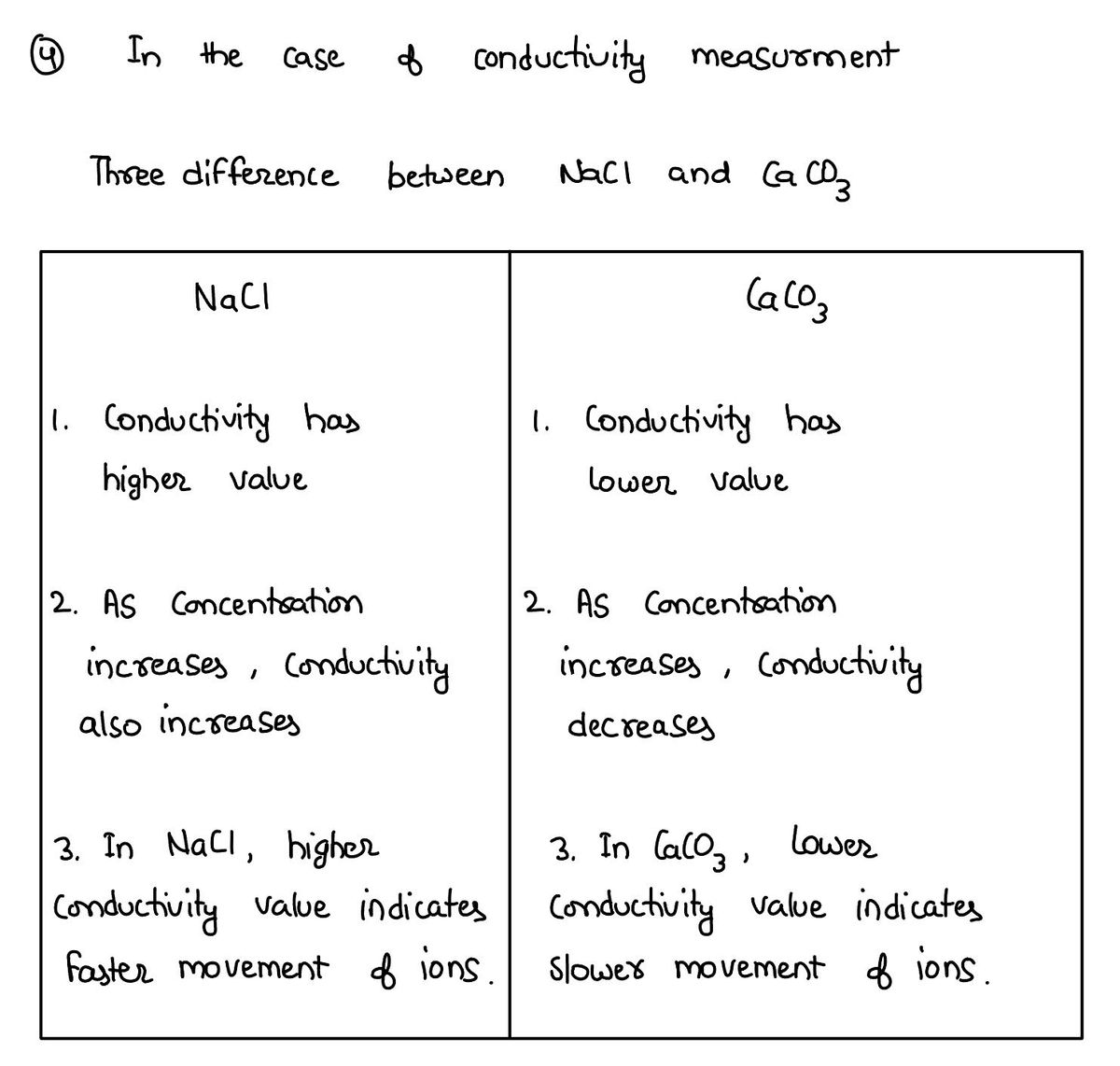
4. 5. 6 In the case of conductivity measurement; find three difference between NaCl and CaCo3. Explain the following terms: a) Strong electrolytes b) Weak electrolytes c) Degree of dissociation Write the conclusion of the experiment.
4. 5. 6 In the case of conductivity measurement; find three difference between NaCl and CaCo3. Explain the following terms: a) Strong electrolytes b) Weak electrolytes c) Degree of dissociation Write the conclusion of the experiment.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Objective
DETERMINE ION CONCENTRATION IN A SOLUTION
1. Determine the various conductivity of serial sodium chloride solution and calcium
carbonate solution.
Observe the relationship between conductivity and concentration in a solution.
2.
Introduction
Conductivity is the ability of a solution to pass an electric current. Compounds dissolved in water
will take up ionized state. These electrically changed ions enable the passage of current through
the solution.
The electric conductivity of aqueous solutions depends on several parameters:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Concentration of the solution
Degree of dissociation of the substance
Mobility of the ions
Charge of the ions
Measurement of the conductivities of the same electrolyte at different concentrations enables
several important characteristic data of the substance to be determined. Also conductivity is used
to determine the purity of a solution or to indicate the total of concentration of all various ions in
that solution.
Conductivity can be used to measure concentration of a compound dissolved in water; the level of
conductivity referred to standard tables or graphs (calibration curve) that convert this to
concentration.

Transcribed Image Text:Evaluation
1.
4.
5.
6
Record the data in tables below.
No
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
NaCl 0.5 mol/L
NaCl 1.0 mol/L
Sample contains NaCl
CaCo3 0.5 mol/L
CaCo3 1.0 mol/L
Sample contains CaCo3
Conductivity in (mS/cm)
26
27
54
0.147
0.078
0.071
In the case of conductivity measurement; find three difference between NaCl and CaCo3.
Explain the following terms:
a) Strong electrolytes
b) Weak electrolytes
c) Degree of dissociation
Write the conclusion of the experiment.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY