38. Consider the following reaction: H;(g) + Iz(g) =2HI(g) Complete the table. Assume that all concentrations are equilib- rium concentrations in M. T(C) [H2] (HI) 25 0.0355 0.0388 0.922 340 0.0455 0.387 9.6 445 0.0485 0.0468 50.2
38. Consider the following reaction: H;(g) + Iz(g) =2HI(g) Complete the table. Assume that all concentrations are equilib- rium concentrations in M. T(C) [H2] (HI) 25 0.0355 0.0388 0.922 340 0.0455 0.387 9.6 445 0.0485 0.0468 50.2
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
![**Chemical Equilibrium and Temperature Dependence**
**Reaction:**
\[
\text{H}_2(g) + \text{I}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 \text{HI}(g)
\]
**Objective:**
Complete the table. Assume that all concentrations are equilibrium concentrations in molarity (M).
**Data Table:**
| Temperature (T°C) | \([\text{H}_2]\) | \([\text{I}_2]\) | \([\text{HI}]\) | \(K_c\) |
|-------------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|------|
| 25 | 0.0355 | 0.0388 | 0.922 | — |
| 340 | — | 0.0455 | 0.387 | 9.6 |
| 445 | 0.0485 | 0.0468 | — | 50.2 |
**Explanation:**
- **\[T (°C)\]:** This column shows the temperature at which the equilibrium concentrations are measured.
- **\([\text{H}_2]\), \([\text{I}_2]\), \([\text{HI}]\):** These columns represent the equilibrium molar concentrations of hydrogen (\(\text{H}_2\)), iodine (\(\text{I}_2\)), and hydrogen iodide (\(\text{HI}\)).
- **\(K_c\):** This column is for the equilibrium constant at the given temperature, which is a measure of the extent of the reaction at equilibrium.
At different temperatures, the equilibrium constant \(K_c\) and the concentrations of the reactants and products can change, illustrating the dynamic nature of equilibrium and its dependence on temperature.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F8a4554f8-c4a9-4782-b993-e17cc0d7a5f8%2Ffbaf61de-7e43-4dc8-b738-6a6b6b9ebda9%2Fnfewsnw_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Chemical Equilibrium and Temperature Dependence**
**Reaction:**
\[
\text{H}_2(g) + \text{I}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 \text{HI}(g)
\]
**Objective:**
Complete the table. Assume that all concentrations are equilibrium concentrations in molarity (M).
**Data Table:**
| Temperature (T°C) | \([\text{H}_2]\) | \([\text{I}_2]\) | \([\text{HI}]\) | \(K_c\) |
|-------------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|------|
| 25 | 0.0355 | 0.0388 | 0.922 | — |
| 340 | — | 0.0455 | 0.387 | 9.6 |
| 445 | 0.0485 | 0.0468 | — | 50.2 |
**Explanation:**
- **\[T (°C)\]:** This column shows the temperature at which the equilibrium concentrations are measured.
- **\([\text{H}_2]\), \([\text{I}_2]\), \([\text{HI}]\):** These columns represent the equilibrium molar concentrations of hydrogen (\(\text{H}_2\)), iodine (\(\text{I}_2\)), and hydrogen iodide (\(\text{HI}\)).
- **\(K_c\):** This column is for the equilibrium constant at the given temperature, which is a measure of the extent of the reaction at equilibrium.
At different temperatures, the equilibrium constant \(K_c\) and the concentrations of the reactants and products can change, illustrating the dynamic nature of equilibrium and its dependence on temperature.
Expert Solution
Step 1
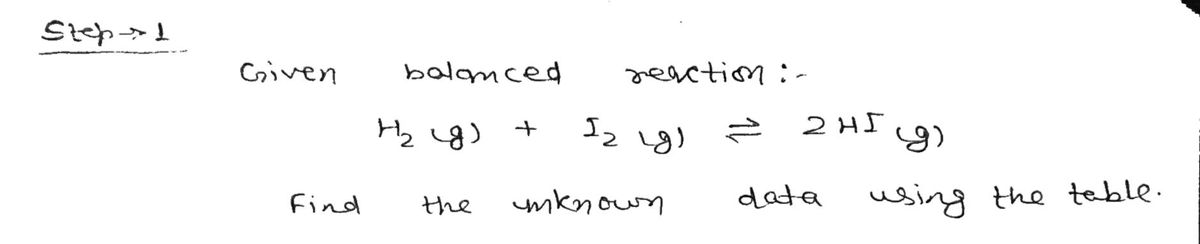
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY