3. The principle of work and energy. A particle of mass m moves along a curve under the action of a force F. If the speed of the particle at time t is v(t), its kinetic energy is defined to be mu². Prove that the change in kinetic energy in any time interval is equal to the work done by F during this time interval.
Q: what is the kinetic energy of the car at point B?
A: given car mass= 2000kg h(i)=30m h(f)=15m kinetic energy initial KEi=0 at point B -kinetic energy…
Q: If a particle is released from x = a, what is the minimum amount of kinetic energy required such…
A:
Q: An object is released at the top of a ramp and slides down it. If the ramp is frictionless does the…
A:
Q: -kx³. The work required to stretch the 0 to the stretched length x = l is Wo. In terms of A "stiff"…
A:
Q: You are planning a deep space exploration and want to take your cat with you. If your spacecraft…
A: cat weighs 8.5 lbf= 37.8099 N velocity of the spacecraft, v=87100×c=0.87 c The rest mass,…
Q: 2. A 1.0 kg particle is moving at a speed of 4.0 m/s at t = 0 s. The kinetic energy of the particle…
A:
Q: A proton (mass m = 1.67 x 1027 kg) is being accelerated along a straight line at 4.60 x 1010 m/s in…
A:
Q: If an object with a mass of 1.8 kg changes it speed from 4.07 m/s to 9.05 m/s, what is its change in…
A: Kinetics energy is given as K.E=12mv2…
Q: An 8.0 kg object is moving in the +x-axis direction. When it passes through x = 0, a constant force…
A: Given, m = 8 kg when x = 0 m, K1 = 30 J K = 0.5 mv2 therefore, v12 = 2K/m v1=2Km = 2×308 = 2.74…
Q: Object A and B have 25 J of kinetic energy. Object B has one-quarter the mass of object A. a.…
A: Kinetic energy of obejct A and B is Mass of obejct B is Work done on each object is Find:(a) The…
Q: A force F of strength 20 N acts on an object of mass 3 kg as it moves a distance of 4 m. If F is…
A: Given value--- force = 20 N. mass = 3 kg. displacement = 4 m. We have to find--- work it does is…
Q: A spring of negligible mass has force constant kkk = 800 N/mN/m. How far must the spring be…
A:
Q: A particle has a function for Potential Energy as shown below. U = (7.30 J/m1) x1 + (9.40 J/m4) x4…
A: Given: U=7.30 Jmx+9.40 Jm4x4 The expression for force (F) on the particle is: F=-dUdx Substitute all…
Q: If an object with a mass of 1.6 kg changes it speed from 4.53 m/s to 8.27 m/s, what is its change in…
A:
Q: Consider a 4.304.30 kg box sliding down a ramp. The box starts from rest at a maximum height of…
A: mass of box (m)= 4.30 kg Initial velocity (u) = 0 msInitial height (h) = 9.50 m Initial…
Q: changes
A: The change in kinetic energy can be calculated using the formula:ΔKE = 1/2 * m * (vf^2 - vi^2)Where:…
Q: A car whose weight is 20,000 N (meaning that its mass is about 2000 kg) is travelling at constant…
A:
Q: A box of mass 4.0 kg hangs by a cable from the ceiling of an elevator. The elevator is moving up at…
A: A box of mass 4 kg is hanging from the ceiling of an elevtorThe elevator is moving with a uniform…
Q: 2. Ryan having mass 60 kg possesses a kinetic energy of 1.3 kJ. What is his speed?
A: Disclaimer - You have asked multiple questions, so as per our guidelines we will answer the first…
Q: Suppose an acorn with a mass of 3.17g falls off a tree. At a particular moment during the fall, the…
A: Given data: Mass (m) = 3.17 g Kinetic energy (KE) = 0.309 J Potential Energy (PE) = 0.157 J…
Q: 4. A force with magnitude F = 10 N with a fixed orientation is applied on a particle. The particle…
A: Since you have posted a question with a multiple sub parts, we will solve first three sub - parts…
Q: 2 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. A proton (mass m = 1.67 x 1027 kg) is being…
A:
Q: 1.A mass is attached to the bottom of a vertical spring. This causes the spring to stretch and the…
A:
Q: If an object with a mass of 2 kg changes it speed from 3.12 m/s to 7.96 m/s, what is its change in…
A: Given data: Mass of the object: Initial speed: Final speed: Concept: The change in kinetic energy…
Q: A horizontal carousel is rotating around its axis with constant angular velocity w. On the carousel…
A: As the angular speed of the cart is omega and its constant, Its speed will increase when it moves…
Q: A 71 kg student traveling in a car with a constant velocity has a kinetic energy of 1.8 x 10^4 J.…
A: We know thatK.E=12mV2V=2(K.E)mHereV=velocity of objectK.E=kinetic energy of objectm=mass of object
Q: A child of mass m = 29 kg slides down a slide of height h = 2.4 m without friction. Let…
A: A) At the top of the slide, the velocity of the child is zero. Write the expression for the total…
Q: 3) Is it possible for a system to have negative potential energy? A. Yes, as long as the kinetic…
A:
Q: A student argues that "no force can move a body of any mass because action and reaction forces are…
A: 1) Given statement : "no force can move a body of any mass because action and reaction forces are…
Q: Consider an object of mass m = 2 kg on a frictionless table. The object experiences a repulsive…
A:

Solution:
A particle of mass m moves along the curve under the action of force vector F. Let us take a and b are two points in the curve. The work done by the force on the particle is
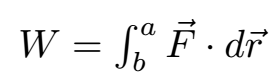
Let us evaluate the scalar product in the integral
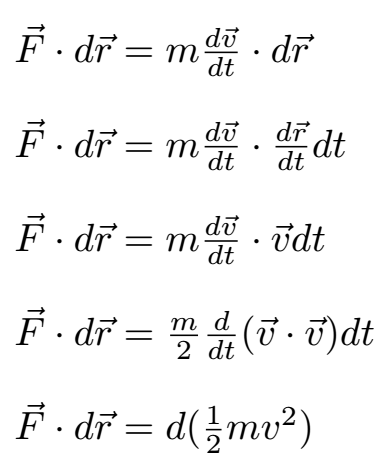
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

- A 3 kg object is moving to the right at a speed of 10ms10ms. The initial kinetic energy of the object is Answer J. A constant force is applied to the left until the object comes to a stop. The final kinetic energy of the object is AnswerThe force shown in the figure(Figure 1) acts on a 1.3-kg object whose initial speed is 0.35 m/s and initial position is x=0.27m. a. Find the speed of the object when it is at the location x=0.99 m. b. At what location would the object's speed be 0.25 m/s?A 15-gram [g] rubber ball is released from a height of 8 meters [m] above a flat surface on the moon. Gravitational acceleration on the moon is 1.62meters per second squared [m/s2]. Assume that no energy is lost from frictional drag. What is the velocity, in units of meters per second [m/s], of the rubber ball the instant before it strikes the flat surface?
- While leaning out a window that is 6.4 m above the ground, you drop a 0.60 kg basketball to a friend at ground level. Your friend catches the ball at a height of 1.9 m above the ground. Determine the following. a)the amount of work done (in J) by the force of gravity on the ball. b) the gravitational potential energy (in J) of the ball-earth system, relative to the ground when it is released. c) the gravitational potential energy (in J) of the ball-earth system, relative to the ground when it is caught. d) the ratio of the change (PEf − PE0) in the gravitational potential energy of the ball-earth system to the work done on the ball by the force of gravityIf an object with a mass of 1.8 kg changes it speed from 3.15 m/s to 8.8 m/s, what is its change in kinetic energy? Assume that the answer has proper SI Units.Do not use Ug=mgh. Please
- A diver of mass 68 kg stands on a diving board 5.0 m above a pool. At the moment of the jump, the diving board transfers its 3400 J of energy to the diver, who leaves the board at an angle of 35°. a. What is the speed of the diver just before they enter the water? b. Suppose that when the diver enters the water, they experience an acceleration of a->water= +4 m/ss J. What is the minimum depth of the pool necessary so that this diver comes to rest exactly at the bottom of the poolA 4.25 kilogram mass slides down a 2.50 meter long ramp which is tilted at an angle of 22.0 degrees. Use the net work to determine the speed of the mass when it reaches the bottom of the ramp. Assume that the mass starts from rest at the top of the ramp. I have found the net work to be 39.1 J. I just don't know how to find the velocity they are looking for.A crate with mass m = 33.3 kg being pushed up an incline that makes an angle φ = 22.7 degrees with horizontal. The pushing force is horizontal, with magnitude P, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the incline is μ = 0.358. Consider the work done on the crate as it moves a distance d = 5.32 m at constant speed. a. What is work done by the pushing force, in joules? b. What is the work done by friction, in joules? c. What is the work done by gravity, in joules? d. What is the net work, in joules?
- a. Calculate the work done (in J) on a 1550 kg elevator car by its cable to lift it 39.5 m at constant speed, assuming friction averages 135 N. b. What is the work done (in J) on the lift by the gravitational force in this process? c. What is the total work done (in J) on the lift?3. A 60 kg snowboarder begins to slide down the hill 50 m high on a smooth surface with a radius curvature of 80 m. The next section (AB) is a 20 m flat rough track with u = .3, at the end of which there is an elastic barrier with k = 1000 N/m. Find her speed at point A. b. How much work is done by frictional force? c. What is the maximum compression of the spring? d. Find the rate of heat dissipation along the section AB. e. How long does it take to cover the section AB? а. h k В1. A 2 kg block slides on a frictionless surface at 10 m/s. How much kinetic energy does it have? 2. A 20 kg crate is lifted 200 m above the ground in 5 minutes. (a) How much work is required to lift it 200m into the air? (b) what is the average power exerted on the crate? 3. A 10 kg block slides down a hill that is 200 meters tall with an initial speed of 12 m/s. What is the final speed of the block when it reaches the bottom of the hill assuming no friction? 4. A 5 kg book is held 10 meters above the floor. How much gravitational potential energy does it have?