3. Let f: R2 → R2 where f(x, y) = (x²y, 3x + 2y), c = (1,1), and u = (1, 1). Use the e-d definition to prove Lu=? (you need to find Lu in your scratchwork).
3. Let f: R2 → R2 where f(x, y) = (x²y, 3x + 2y), c = (1,1), and u = (1, 1). Use the e-d definition to prove Lu=? (you need to find Lu in your scratchwork).
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
3. Let \( f : \mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}^2 \) where \( f(x, y) = (x^2y, 3x + 2y) \), \( c = (1, 1) \), and \( u = (1, 1) \). Use the \(\epsilon\)-\(\delta\) definition to prove \( L_u = ? \) (you need to find \( L_u \) in your scratchwork).
![**Example:**
Let \( f: \mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}^2 \), where \( f(x, y) = \begin{pmatrix} x^2 y \\ 3x + 2y \end{pmatrix} \). Consider \( u = (1, 0) \) and \( c = (1, 1) \).
**Claim:** \( Lu = (2, 3) \)
**Proof:**
Fix \(\varepsilon > 0\). Choose \(\delta = \frac{\varepsilon}{2}\). Assume \(0 < |t| < \delta\). Then:
\[
\left\| \frac{1}{t} \left[ f(c + tu) - f(c) \right] - Lu \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} f(1+t, 1) \\ (1.5) \end{pmatrix} - (2, 3) \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} (1 + t)^2 \\ 3(1 + t) + 2 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 1.5 \end{pmatrix} \right\| - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} (1 + 2t + t^2) \\ 3t + 5 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 1.5 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} 2t + t^2 \\ 3t \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \begin{pmatrix} t, 0 \end{pmatrix} \right\| = |t](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F79599c56-a340-49a0-b0ff-829b3947a798%2F406d3e92-8ad4-42f4-962a-01c845200bdb%2Fq4q60oxm_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Example:**
Let \( f: \mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}^2 \), where \( f(x, y) = \begin{pmatrix} x^2 y \\ 3x + 2y \end{pmatrix} \). Consider \( u = (1, 0) \) and \( c = (1, 1) \).
**Claim:** \( Lu = (2, 3) \)
**Proof:**
Fix \(\varepsilon > 0\). Choose \(\delta = \frac{\varepsilon}{2}\). Assume \(0 < |t| < \delta\). Then:
\[
\left\| \frac{1}{t} \left[ f(c + tu) - f(c) \right] - Lu \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} f(1+t, 1) \\ (1.5) \end{pmatrix} - (2, 3) \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} (1 + t)^2 \\ 3(1 + t) + 2 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 1.5 \end{pmatrix} \right\| - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} (1 + 2t + t^2) \\ 3t + 5 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 1.5 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \frac{1}{t} \begin{pmatrix} 2t + t^2 \\ 3t \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 2, 3 \end{pmatrix} \right\|
\]
\[
= \left\| \begin{pmatrix} t, 0 \end{pmatrix} \right\| = |t
Expert Solution
Step 1
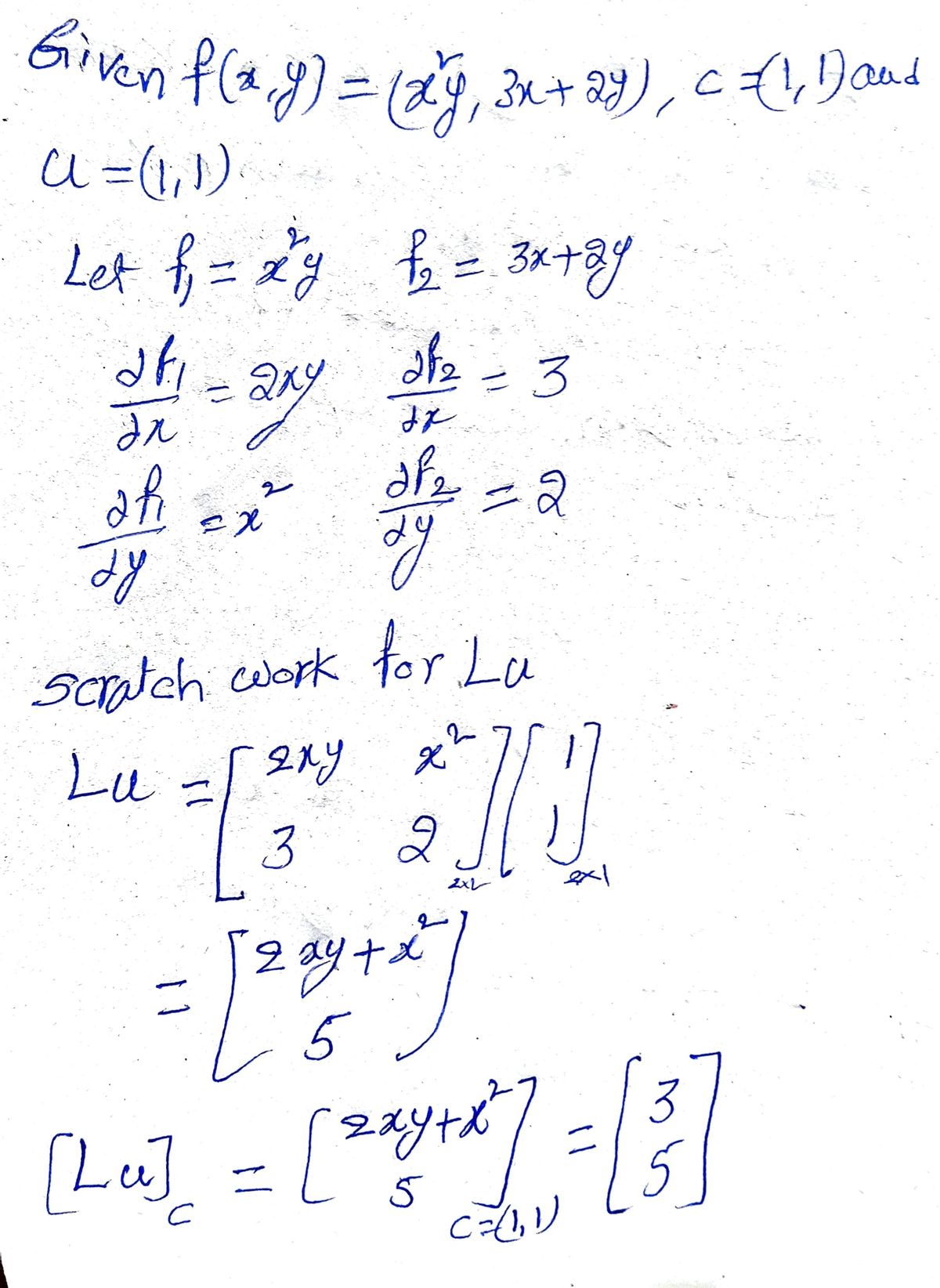
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

