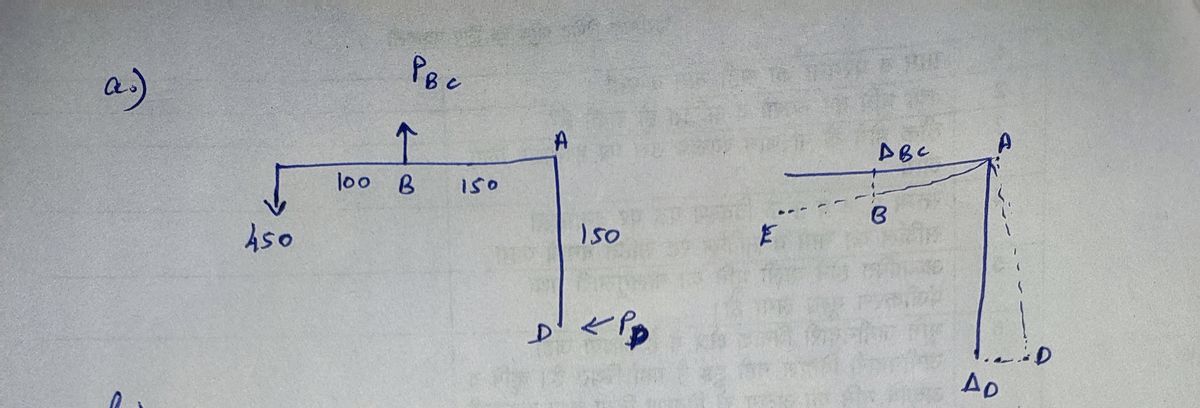
3) The rigid link is supported by steel wire (1) with an unstretched length of 200 mm and cross-sectional area of 22.5 mm2. Member (2) is a short aluminum of initial length 50 mm and cross-sectional area of 40 mm?. The modulus of elasticity of the steel wire is 200 GPa and the aluminum block is 70 GPa. a) Draw the deflected shape of the rigid member and clearly label the deformation of members (1) and (2). b) Write the equilibrium and compatibility equations needed to solve the problem along with the supporting sketches. Hint: Be sure to carefully consider if the members are elongating or shortening; this must be represented mathematically. c) Calculate the internal forces in both axial members and clearly indicate tension or compression. [Ans. to Check: F2 = 535 N]
3) The rigid link is supported by steel wire (1) with an unstretched length of 200 mm and cross-sectional area of 22.5 mm2. Member (2) is a short aluminum of initial length 50 mm and cross-sectional area of 40 mm?. The modulus of elasticity of the steel wire is 200 GPa and the aluminum block is 70 GPa. a) Draw the deflected shape of the rigid member and clearly label the deformation of members (1) and (2). b) Write the equilibrium and compatibility equations needed to solve the problem along with the supporting sketches. Hint: Be sure to carefully consider if the members are elongating or shortening; this must be represented mathematically. c) Calculate the internal forces in both axial members and clearly indicate tension or compression. [Ans. to Check: F2 = 535 N]
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![3) The rigid link is supported by steel wire (1) with an unstretched length of 200 mm and cross-sectional
area of 22.5 mm?. Member (2) is a short aluminum of initial length 50 mm and cross-sectional area of
40 mm?. The modulus of elasticity of the steel wire is 200 GPa and the aluminum block is 70 GPa.
a) Draw the deflected shape of the rigid member and clearly label the deformation of members (1)
and (2).
b) Write the equilibrium and compatibility equations needed to solve the problem along with the
supporting sketches. Hint: Be sure to carefully consider if the members are elongating or
shortening; this must be represented mathematically.
c) Calculate the internal forces in both axial members and clearly indicate tension or compression.
[Ans. to Check: F2 = 535 N]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fac9fa3d1-27a5-4e30-906e-905604004d91%2Fe2a16978-b88e-4efd-af98-5988fd9a6730%2Fmti9zk5_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:3) The rigid link is supported by steel wire (1) with an unstretched length of 200 mm and cross-sectional
area of 22.5 mm?. Member (2) is a short aluminum of initial length 50 mm and cross-sectional area of
40 mm?. The modulus of elasticity of the steel wire is 200 GPa and the aluminum block is 70 GPa.
a) Draw the deflected shape of the rigid member and clearly label the deformation of members (1)
and (2).
b) Write the equilibrium and compatibility equations needed to solve the problem along with the
supporting sketches. Hint: Be sure to carefully consider if the members are elongating or
shortening; this must be represented mathematically.
c) Calculate the internal forces in both axial members and clearly indicate tension or compression.
[Ans. to Check: F2 = 535 N]
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning