3-37E A spring-loaded piston-cylinder device is initially filled with 0.2 lbm of an R-134a liquid-vapor mixture whose temperature is -30°F and whose quality is 80 percent. The spring constant in the spring force relation F= kx is 37 lbf/in, and the piston diameter is 12 in. The R-134a undergoes a process that increases its volume by 40 percent. Calculate the final temperature and enthalpy of the R-134a. Answers: 81.5°F, 120 Btu/lbm W Fluid -D- FIGURE P3-37E Spring
3-37E A spring-loaded piston-cylinder device is initially filled with 0.2 lbm of an R-134a liquid-vapor mixture whose temperature is -30°F and whose quality is 80 percent. The spring constant in the spring force relation F= kx is 37 lbf/in, and the piston diameter is 12 in. The R-134a undergoes a process that increases its volume by 40 percent. Calculate the final temperature and enthalpy of the R-134a. Answers: 81.5°F, 120 Btu/lbm W Fluid -D- FIGURE P3-37E Spring
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website:**
**Problem 3-37E:**
A spring-loaded piston-cylinder device is initially filled with 0.2 lbm of an R-134a liquid-vapor mixture whose temperature is -30°F and whose quality is 80 percent. The spring constant in the spring force relation \( F = kx \) is 37 lbf/in, and the piston diameter is 12 in. The R-134a undergoes a process that increases its volume by 40 percent. Calculate the final temperature and enthalpy of the R-134a.
**Answers:** 81.5°F, 120 Btu/lbm
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram labeled "FIGURE P3-37E" shows a vertical piston-cylinder device. Inside the cylinder, a spring is positioned above a fluid labeled as "Fluid." This represents the R-134a liquid-vapor mixture. The spring is compressed initially, indicating a potential for expansion. The cylinder has a defined piston diameter marked as \( D \).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 23 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
This is the only Superheated R-134a property table we are given, how do we find the final state of R-134a the superheated state from here?
Thank you
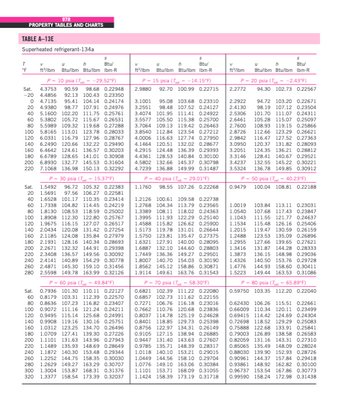
Transcribed Image Text:# Superheated Refrigerant-134a: Property Tables and Charts
## TABLE A-13E
This table provides thermodynamic properties of superheated refrigerant-134a at various pressures and temperatures. The properties listed are:
- **T (°F)**: Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
- **\( u \) (Btu/lbm)**: Specific internal energy in British thermal units per pound mass.
- **\( h \) (Btu/lbm)**: Specific enthalpy in British thermal units per pound mass.
- **\( s \) (Btu/lbm R)**: Specific entropy in British thermal units per pound mass per degree Rankine.
The table is divided into different sections, each for a specific pressure:
- **\( P = 10 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = -29.52°F)**
- **\( P = 15 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = -14.15°F)**
- **\( P = 20 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 2.43°F)**
- **\( P = 30 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 15.37°F)**
- **\( P = 40 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 29.91°F)**
- **\( P = 50 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 40.37°F)**
- **\( P = 60 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 49.84°F)**
- **\( P = 70 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 58.30°F)**
- **\( P = 80 \text{ psia} (T_{\text{sat}} = 65.89°F)**
### Explanation of Data Columns:
- **Sat.**: Denotes properties at saturation condition.
- **Temperature (T°F)**: Represents the temperature at which the properties are measured.
- **Specific Internal Energy (\( u \))**: Energy contained within the refrigerant due to the motions and interactions of its molecules.
- **Specific Enthalpy (\( h \))**: Total heat content of the refrigerant, including internal energy and the product of pressure and volume.
-
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY