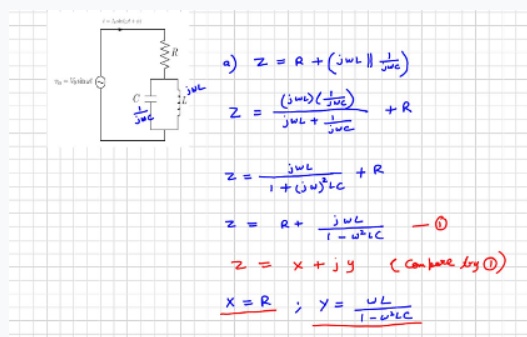
2. Consider the LRC circuit below. Vin Vo sin wt i lo sin(wt + o) C www R L (a) Find an analytic expression for the equivalent impedance of the R, L, and C combination. Remember that Zc = 1/(jwC) and ZL = jwL and that you can combine impedances in series and parallel the same way that you would combine resistances. Give your answer in the form Z = X+jY (i.e. find X and Y). (b) The current in the resistor is given by i = Io sin(wt + o). Find Io and tano in terms of Vo, w, R, L, and C. (c) Plot VR/Vo as a function of frequency. VR represents the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor. Use component values L = 300 μH, C = 15 μF, and R = 1000 2 and plot over a frequency range of f= 2200-2500 Hz. Don't forget that w 2πf. Don't draw your graph by hand, use plotting software. (d) What is the impedance of the parallel LC part of the circuit when w=1/√LC? Compare this to the impedance of a series combination of L and C when w=1/√LC.
2. Consider the LRC circuit below. Vin Vo sin wt i lo sin(wt + o) C www R L (a) Find an analytic expression for the equivalent impedance of the R, L, and C combination. Remember that Zc = 1/(jwC) and ZL = jwL and that you can combine impedances in series and parallel the same way that you would combine resistances. Give your answer in the form Z = X+jY (i.e. find X and Y). (b) The current in the resistor is given by i = Io sin(wt + o). Find Io and tano in terms of Vo, w, R, L, and C. (c) Plot VR/Vo as a function of frequency. VR represents the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor. Use component values L = 300 μH, C = 15 μF, and R = 1000 2 and plot over a frequency range of f= 2200-2500 Hz. Don't forget that w 2πf. Don't draw your graph by hand, use plotting software. (d) What is the impedance of the parallel LC part of the circuit when w=1/√LC? Compare this to the impedance of a series combination of L and C when w=1/√LC.
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:In class we showed that any complex number Z can be written in either of the following two forms:
Z = X+jY
Z = |Z| ej
To go between these two forms, you can use the following relationships:
|Z| = √X² +Y²
Y
X
X = |Z| cos o
Y = |Z| sino
We also introduced one more quantity called the complex conjugate of Z, which is denoted Z*. To
find the complex conjugate of Z, you simply reverse the sign in front of all the j's. So, for example,
if:
Z = X+jY= |Z| e¹
then:
tan o =
Z* = X-jY= |Z| e-j
The complex conjugate is useful because it can be used to calculate |Z|, the magnitude of Z.
Consider, for example, the following product:
ZZ* = (x+jY) (X -jY) = x² + y² = |Z|².
Alternatively, using the exponential form of Z:
ZZ = (|Z|e¹) (|Z| e-jº) = |Z|².
In both cases we get that ZZ* = |Z|².

Transcribed Image Text:2. Consider the LRC circuit below.
Vin = Vo sin wt
i = lo sin(wt + o)
C
R
L
(a) Find an analytic expression for the equivalent impedance of the R, L, and C combination.
Remember that Zc = 1/(jwC) and Zz = jwL and that you can combine impedances in series and
parallel the same way that you would combine resistances. Give your answer in the form Z = X+jY
(i.e. find X and Y).
(b) The current in the resistor is given by i = Io sin(wt + o). Find Io and tan o in terms of Vo, w,
R, L, and C.
(c) Plot VR/Vo as a function of frequency. VR represents the amplitude of the voltage across the
resistor. Use component values L = 300 µH, C = 15 µF, and R = 1000 2 and plot over a frequency
range of f = 2200-2500 Hz. Don't forget that w 2πf. Don't draw your graph by hand, use
plotting software.
=
(d) What is the impedance of the parallel LC part of the circuit when w=1/√LC? Compare this
to the impedance of a series combination of L and C when w=1/√LC.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,