2. Consider a woman who earns $10 per hour and who does not have non-labour income (V=0). a. Assume that there are 168 hours in a week, draw her weekly budget constraint. Label the x-axis, the y-axis, the x-intercept, the y-intercept, the slope and the endowment point. b. Suppose that this woman has one child, is eligible for welfare, and can receive up to $200/week from the local welfare agency. These benefits, however, are reduced by 50 cents for every dollar she earns. In other words, if E = weekly earnings, welfare benefits = 200-.5E. On the same graph as above, show how the welfare program affects her budget constraint. Be sure to label the slope of her new budget constraint. c. How many hours a week can this woman work before her weekly welfare benefits are equal to zero? d. Consider a woman who has a wage of $10 per hour and who, in the absence of a welfare program, works 20 hours per week. Assuming that this woman has one child and is eligible for welfare, what will the effect of the above mentioned welfare program be on the number of hours per week that she chooses to work. On your graph, illustrate the income effect, the substitution effect and the total effect. e. Give a brief intuitive explanation for why the substitution effect and the income effect work in the same direction.
2. Consider a woman who earns $10 per hour and who does not have non-labour income (V=0).
a. Assume that there are 168 hours in a week, draw her weekly budget constraint. Label the x-axis, the y-axis, the x-intercept, the y-intercept, the slope and the endowment point.
b. Suppose that this woman has one child, is eligible for welfare, and can receive up to $200/week from the local welfare agency. These benefits, however, are reduced by 50 cents for every dollar she earns. In other words, if E = weekly earnings, welfare benefits = 200-.5E. On the same graph as above, show how the welfare program affects her budget constraint. Be sure to label the slope of her new budget constraint.
c. How many hours a week can this woman work before her weekly welfare benefits are equal to zero?
d. Consider a woman who has a wage of $10 per hour and who, in the absence of a welfare program, works 20 hours per week. Assuming that this woman has one child and is eligible for welfare, what will the effect of the above mentioned welfare program be on the number of hours per week that she chooses to work. On your graph, illustrate the income effect, the substitution effect and the total effect.
e. Give a brief intuitive explanation for why the substitution effect and the income effect work in the same direction.
Hello. Since your question has multiple sub-parts, we will solve the first three sub-parts for you. If you want remaining sub-parts to be solved, then please resubmit the whole question and specify those sub-parts you want us to solve.
c) This women works before her weekly benefits get equal to zero for,
=Total hour –Hour spends in leisure at point B where the benefit becomes equal to zero
=168 – 128
=40 hours a week
Given,
Wages rate (w) = $ 10 per hour
Non labor income = 0
a)
Total hours (T) = 168 hours
If a woman does not work at all, she will spend 168 hours in leisure.
Leisure(r) = 168 hours
If she works for 168 hours, she will earn
Income (M) = Time * wage rate = T*w
= 168*10 = 1680
Using this income, she can consume C amount by assuming price equal to $1.
The budget constraint,
w r+ C = M
10 r+ C=1680
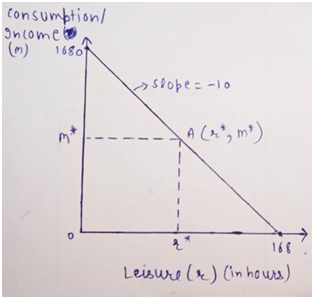
The x-axis shows the leisure and the y-axis shows the total income or consumption.
X intercept shows maximum hour spend in leisure = 168
Y intercept shows maximum income= 1680
The slope of the budget line = -Change in income /Change in hours =-ΔM/ΔT
=1680/168 =-10
The point A shows the endowment point where this woman earns M* income by working for T-r hours and hours spend in leisure (r*).
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images








