2. A photon is emitted from a hydrogen atom that undergoes an electronic transition from the state n =3 to the state n =2. Calculate (a) the energy, (b) the wavelength, and (c) the frequency of the emitted photon.
Q: 1. In a certain hydrogen atom you know that it undergoes a transition from a state with n = 3 to a…
A:
Q: 6. Use Boltzmann distribution to solve this problem. A system consists of 3,000 particles that can…
A: Given: A system consists of 3000 particles T = 900 k Formula used:NjNi = gj e-εjkTgi e-εikT
Q: 41. A hydrogenic atom makes a transition from an energy level given by n What is the (n>…
A:
Q: 2. The Paschen series of emission lines in the H atom spectrum are defined as those for which n₂ = 3…
A:
Q: A photon emitted as a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state.…
A:
Q: 1. A hydrogen atom initially in its ground state (n=1) absorbs a photon and ends up in the state for…
A:
Q: 3. A hydrogen atom is in its ground state (n=1). Using the Bohr theory of the atom, calculate (a)…
A: We know that in hydrogen atom there is only one electron and one proton(charged particles). Electron…
Q: Consider the four lowest energy levels shown in the diagram of a certain atom. How many spectral…
A: An energy state is any discrete value from a set of total energy values for a subatomic particle…
Q: 5. Consider the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom. (a) How much energy (in eV) is needed to cause a…
A: (a)The energy required is given by ΔE=-13.6 eV1nf2-1ni2 Here, nf is the quantum number of the final…
Q: a) Looking at transitions between the first 6 energy levels (n = 1 through n = 6), what is the…
A:
Q: 18. The following transitions are for an electron in a hydrogen atom: I. n = 4 to n = 2 II. n = 1 to…
A: The energy in form of photon is released when an electron transits from a higher level to a lower…
Q: A rubidium atom (atomic mass 85) is initially at room temperature and has a velocity of v = 290 m/s…
A: Given: Initial Velocity,u=290m/sAtomic Mass,A=85gWavelength,λ=780nm=780×10-9mFinal…
Q: 11. Below is the energy level diagram for atomic hydrogen transitions which terminate at the first…
A:
Q: What is the energy of the photon that, when absorbed by a hydrogen atom, could cause an electronic…
A:
Q: 3. Use the Rydberg formula to obtain the wavelength of the 80a radio line for an atom of infinite…
A:
Q: 4. A proton and an electron recombine to form atomic hydrogen in its 4p state. At what wavelengths…
A:
Q: 02. An electron in an excited hydrogen atom has deBroglie wavelength of 13.3182 x 101" m, drops into…
A: Given Data: de-Broglie wavelength, λD=13.3182×10-10 m Falling state is ground state (n1=1) Standard…
Q: 4. An electron in the n = 2 state of hydrogen is excited by absorbing the longest possible…
A: Given, Electron in the n = 2 state of hydrogen is excited by absorbing the longest possible…
Q: 5. A doubly ionized lithium atom is in the ground state. It absorbs energy and makes a transition to…
A:
Q: they all eventually come back down to the ground state (n = 1). How many different wavelengths of…
A:
Q: When the electron in a hydrogen atom falls from n = 7 to the ground state energy level, a photon is…
A:
Q: A particular atom has two energy levels with a transition wavelength of 420 nm. At 297 K there are…
A:

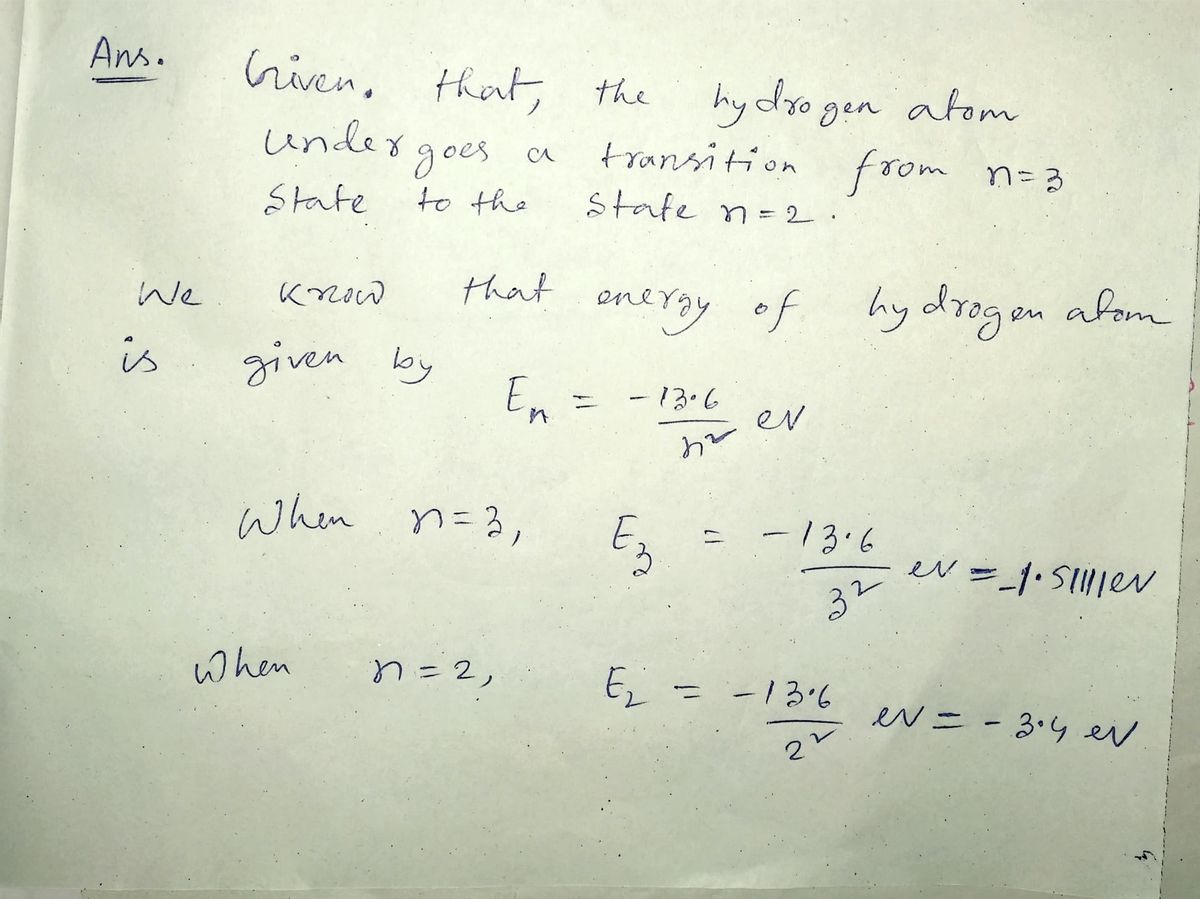
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- 2. Consider an electron in a hydrogen atom that is transitioning from the n = 2 to the n = 6 level.What is the wavelength (in nm) of the photon associated with this transition?1. The two prominent yellow lines in the spectrum of sodium result from transitions to the ground state from the 3p state with the electron spin-up, and from the 3p state with the electron spin-down. The wavelengths these two lines are 589.0 nm and 589.6 nm. (a) Calculate the energies in eV of the photons corresponding to these wavelengths, and the difference in energy of these photons AE. (b) The energy difference you found in part (a) is due to the spin-orbit effect. An electron in the 3p state of sodium experiences an internal magnetic field B, due to the orbital angular momentum. For a magnetic field B₁, the spin-orbit energy splitting is AE = 2µBB₁, where B is the Bohr magneton. Find the orbital magnetic field By from the energy difference AE you found in part (a).11. In the Balmer series, during which of the following energy state changes of the hydrogen atom is the photon with the most energy emitted? (A) n = 5 directly to n = 2 (B) n = 4 directly to n = 2 (C) n = 2 directly to n = 4 (D) n = 2 directly to n = 5 12. What is the minimum energy needed to ionize a hydrogen atom when it is in the n = 2 state? (A) 1.9 eV (B) 3.4 eV (C) 12.2 eV (D) 13.6 eV
- 4. Describe the following energy state transition for an electron in a hydrogen atom. List the energy of the emitted photon, wavelength, its initial and final orbit. (a) n=3 to n = 1, (b) n=6 to n= 2, (c) n = 5 to n=3.Which of these expressions would yield the wavelength of light in meters emitted when an electron drops from orbit n = 3 to n = 2 in a Bohr hydrogen atom? Given h = 4.14 x 10-15 eVs and c = 3.00 x 108 m/s. a. 1.89/hxc b. hc/1.89 c. 1.89 x h x c d. (1.51 + 3.4)/hc e. hc/3.46.An atomic hydrogen atom is immersed in a magnetic field of 12.44 T. For the 2p to 1s transition more than one line will appear due to the Zeeman effect. What is the smallest wavelength separation of these lines? (in units of picometers (pm)).
- 1. Differentiate the three quantum numbers for an electron in the hydrogen atom and justify why the idea of an electron orbiting a proton has been abandoned.7. When an electron transitions from the third excited state to the ground state in a hydrogen atom, the energy emitted in one photon is: A. 12.7 eV B. 10.5 eV C. 3.6 eV D. 0 eV