2) For this problem, refer to the titration chart below 14.0 12.0 100 8.0 pH 6.0 4.0 2.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0 Volume of 0.100 M NaOH, ml. a) How many acidic protons did the titrated acid have? b) If the initial volume of the unknown acid in question was 50ML, what was the concentration of acid? c) Find the pKas of each of the acidic protons. d) Which of the following acids is most likely to be the identity of the unknown acid. i) охalic acid, (рКа 3D 5.4 х 10?, 5.4 x 10-5) ii) sulfurous acid (pKa = 1.7 x 10-2, 6.4 x 10-8) iii) phosphoric acid (pKa = 7.1 x 10-3, 6.3 x 10-8, 4.2 x 10-13)

The titration curve given is as shown below.
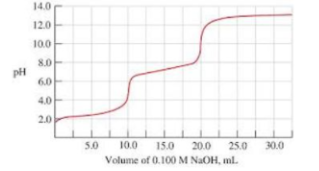
a) From the above titration curve we can see that there are total 2 equivalence points in the titration shown by A and B below.
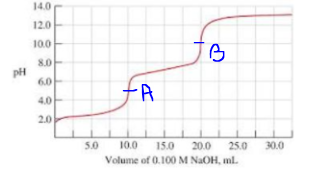
Since there are 2 equivalence points in the titration.
Hence the acid titrated will have 2 acidic protons.
b) Given : Volume of acid solution = 50.0 mL
From the curve we can see that the concentration of NaOH used is 0.100 M and the volume of NaOH solution required to reach final equivalence point i.e B is 20.0 mL.
Since 1 mole of acid will require 2 moles of NaOH for complete neutralisation.
Hence moles of NaOH required = moles of acid present X 2
Since moles = concentration X volume of solution
=> Concentration of NaOH X volume of NaOH solution required = concentration of acid X volume of acid solution X 2
Hence substituting the values we get,
=> 0.100 X 20.0 = concentration of acid X 50.0 X 2
=> concentration of acid = 0.02 M
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images









