10 Use the differential equation approach to find vc(t) f in the circuit in Fig. P7.10. imatsb or bovloa ai 1 whes basenoilibros leiliai sd1.5263 q adi zaos ogsilov Τ Seti4 koloni bsau www 9 ko Jubni sta | 9kΩ ΚΩ
10 Use the differential equation approach to find vc(t) f in the circuit in Fig. P7.10. imatsb or bovloa ai 1 whes basenoilibros leiliai sd1.5263 q adi zaos ogsilov Τ Seti4 koloni bsau www 9 ko Jubni sta | 9kΩ ΚΩ
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
100%
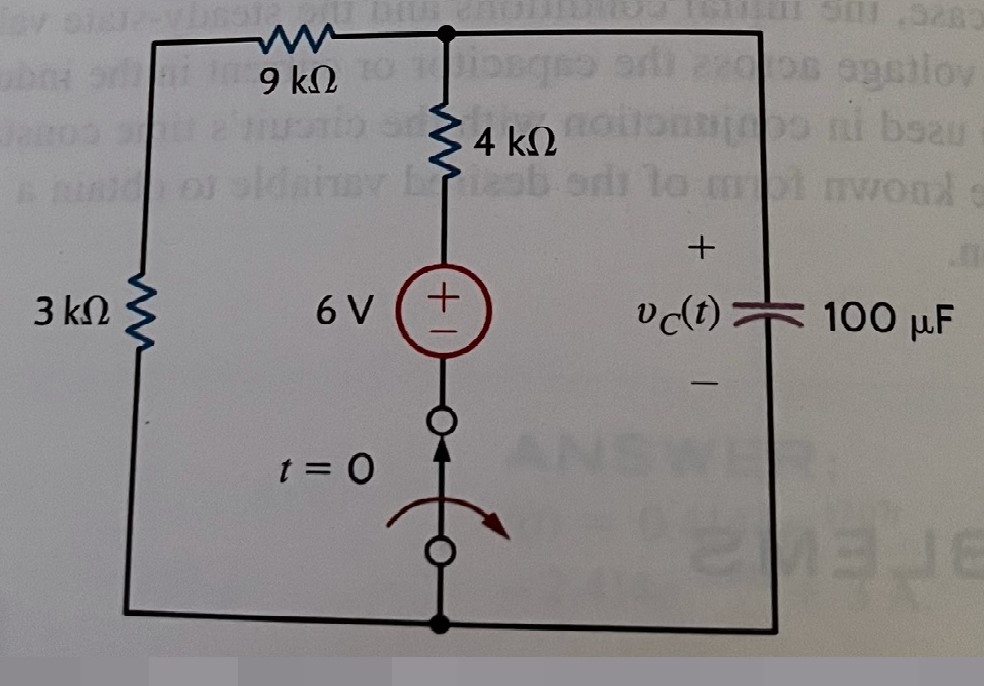
Use the differential equation approach to find vc(t) for t>0 in the circuit in Fig. P7.10.

Transcribed Image Text:**7.10** Use the differential equation approach to find \( v_c(t) \) for \( t > 0 \) in the circuit in Fig. P7.10.
### Circuit Description
The circuit diagram in Figure P7.10 consists of the following components connected in series:
- A 3 kΩ resistor
- A 9 kΩ resistor
- A 4 kΩ resistor
- A DC voltage source of 6 V
- A capacitor of 100 μF, where the voltage across the capacitor is denoted as \( v_c(t) \)
The circuit is initially at \( t = 0 \), suggesting that the switch is closed at this moment, allowing the analysis of transient behavior for \( t > 0 \).
### Diagram Explanation
At \( t = 0 \), the circuit is energized by a 6 V source. The resistors and capacitor are arranged in a series loop. The voltage \( v_c(t) \) across the capacitor is a function of time, which can be analyzed using differential equations to understand how the capacitor charges over time. This setup is typically used to model time-dependent voltage changes in RC circuits.
Expert Solution
Step 1
It is given that:-
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,